Interconnect#
Interconnect is a mechanism for connecting applications deployed at multiple edge sites (clusters).
Interconnect makes use of a local router deployed to the edge alongside the applications to give a Hub and Spoke pattern of links. A client application may connect to the router at the client edge site (the Spoke), which in turn connects to a corresponding router at the server edge site (the Hub), which then connects to the server application.
The routers at the edge sites are responsible for routing the traffic between the client and server applications.
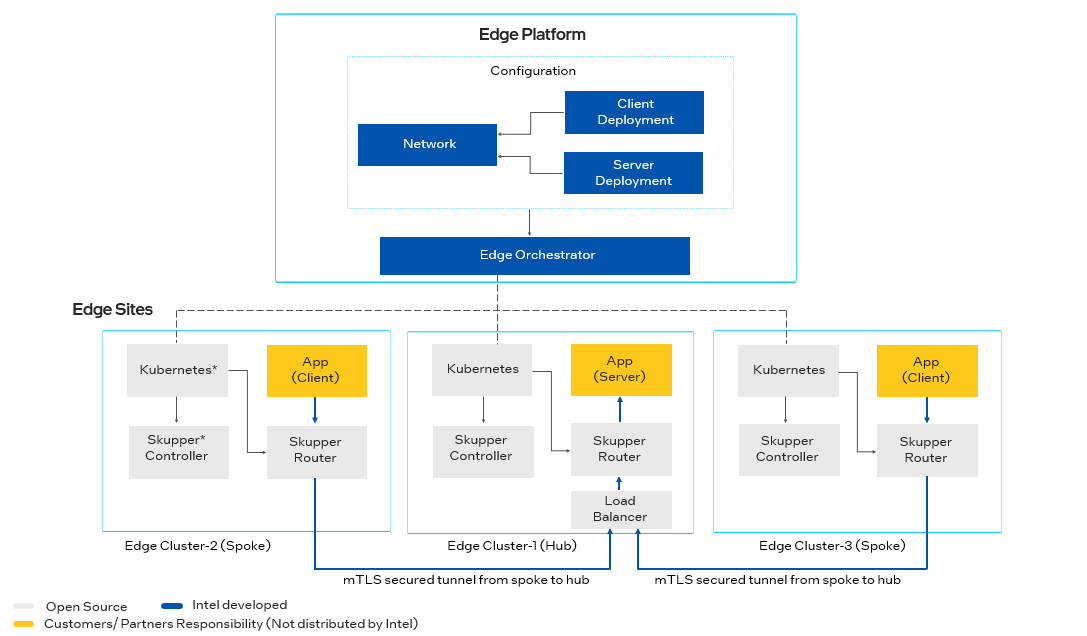
For these instructions, let us assume assume that you have a simple client/server application. You want to deploy the server on one edge cluster, and the client to another edge cluster. Links will be established from the client(s) to the server (Spokes to the Hub).
The Interconnect makes use of an opensource component called Skupper interconnect, described at https://skupper.io. Edge Orchestrator automates the configuration of Skupper interconnect on the Edge clusters.
Perform the following steps to use the Interconnect feature:
Annotate your server application’s service with the following annotations to expose services to the router.
Annotation
Description
network.app.edge-orchestrator.intel.com/expose-service
Set to “true” to expose the service to the router.
network.app.edge-orchestrator.intel.com/expose-port
The port number to expose.
Note
The service must be of type ClusterIP to be exposed to the router.
Following is an example:
apiVersion: v1 Kind: Service metadata: name: my-backend annotations: network.app.edge-orchestrator.intel.com/expose-service: "true" network.app.edge-orchestrator.intel.com/expose-port: "8080" spec: ports: - port: 8080 targetPort: 8080 selector: app: my-backend type: ClusterIP
Without the annotations, the service will not be exposed to the interconnect. The Skupper router will automatically route client requests to this server.
Note
The router will create another service of type Loadbalancer in the interconnect namespace. An IP address will be assigned to this service. Installing the load-balancer extension (see below) facilitates this.
Configure your client to connect to the Skupper router.
Your client application must be configured to connect to the backend as a service on your client’s local cluster. How you configure this depends on your client application, and on the service name you used in your service.
The DNS name of the service is the
http|https://<service name>.<namespace>.svc.cluster.local:<port>
The port is the same as the port number you exposed on the server side.
For example:
backend: address: "http://my-backend.interconnect.svc.cluster.local:8080"
Create a network object. The Graphical User Interface does not support this and must be done using a REST API call.
Note
You must be a member of the Edge-Manager-Group or Edge-Operator-Group for your project as described in Edge Orchestrator Groups and Roles to perform these steps.
Create a JWT using the instructions Obtaining a JSON Web Token (JWT) in Configure Identity and Access Management, which will fill the
JWT_TOKENvariable. Then fill in the variables in the example below and run these commands:export CLUSTER_FQDN=<your-orchestrator-domain-name> export PROJECT_NAME=<your-project-name> export NETWORK_NAME=<choose-a-name-for-your-new-interconnect> cat << EOF > network.json {"description": "Network for Interconnect", "type": "application-mesh"} EOF curl https://api.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/v1/projects/${PROJECT_NAME}/networks/${NETWORK_NAME} \ -X PUT -H "authorization: Bearer ${JWT_TOKEN}" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d @network.json
If you would like to verify the network was created, you can do the following and ensure it is in the returned list:
curl https://api.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/v1/projects/${PROJECT_NAME}/networks \ -H "authorization: Bearer ${JWT_TOKEN}"
Deploy a load balancer on the clusters that will host the server.
The clusters that host your server must be routable from the clusters where you run your clients, and so a LoadBalancer is required. We recommend using the Load-Balancer extension (which uses metallb* opensource project) package to deploy a load-balancer, which can be used by the router. The Load-Balancer is documented in Load Balancer Package.
Note
The Load-Balancer is only needed on the server (Hub) Edge cluster.
Note
During deployment of the Load-Balancer, you should not select the Network created in step 3 (if prompted).
Deploy the Skupper extension on all clusters that will participate in the Interconnect.
This package is available as an extension package (see Enhance Deployments ) in the application catalog. Create a Deployment (see Deployments) that deploys this extension package to all edges that will use the Interconnect.
Note
During deployment of Skupper extension, you must not select the Network created in step 3 (if prompted).
Deploying the server application to use the Interconnect
Follow the typical workflow at Deployments to deploy your server application.
If any networks present (such as the one created above), then an additional page is displayed during the deployment workflow. This page allows you to select the network that your deployment will participate in.
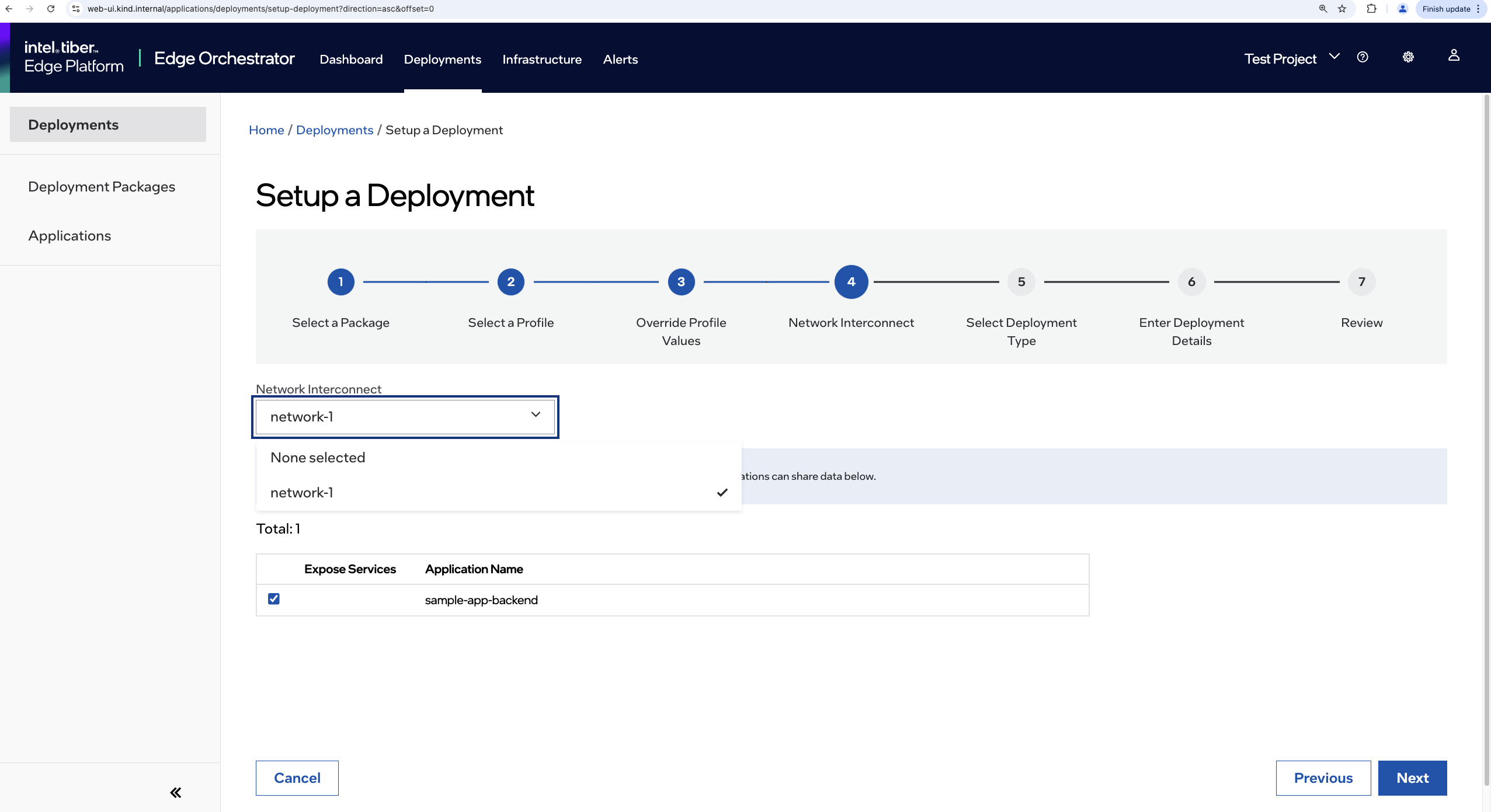
- On this page, select the network that your deployment will participate in.
For example, use the network you created in step 3.
You must also expose the server applications that contain the service(s) that have been annotated in Step 1. Click the checkbox to expose the application(s).
Note
If the application is not exposed in this step, the router will not route traffic to the annotated service.
Deploy the client application to use the Interconnect.
The procedure is identical to step (6), selecting the Network, but not choose any applications to expose.
Best Practices#
It is essential that when deploying the load balancer for your server, that you do not expose this directly to the Internet. The consequence of exposing the load-balancer to the internet is that it could be attacked by malicious actors. How to achieve this network isolation depends on the specific infrastructure you are using. For example, VPNs and Firewalls may be useful.
Using TLS between your applications and the routers is a recommended practice. This is described in https://skupper.io/docs/cli/native-security-options.html. Certificates are placed in the following secrets:
skupper-tls-<deploymentname> - contains tls.crt, tls.key, and ca.crt. To be used by your server to accept connections from the Router.
skupper-tls-client - contains ca.crt. To be used by your client to connect to the Router.
How your application makes use of these secrets is application dependent.
Troubleshooting Interconnect#
If you are having trouble with the Interconnect, the following steps may help:
On the Edge Orchestrator#
To see a list of the Network(s) driving the Interconnect Hub and Spoke pattern:
kubectl get network -o yaml
To see a list of the clusters participating in the Interconnect Hub and Spoke pattern:
kubectl get clusters.interconnect.app.edge-orchestrator.intel.com
To see a list of the links participating in the Interconnect Hub and Spoke pattern, use the following:
kubectl get links.interconnect.app.edge-orchestrator.intel.com
To see a list of the services exposed on the Interconnect, use the following:
kubectl get services.interconnect.app.edge-orchestrator.intel.com
Pods on the Hub or Spoke Edge Node Cluster#
To see a list of the pods in the interconnect namespace (where the router is running):
kubectl -n interconnect get all
There should be two pods skupper-service-controller and skupper-router.
The skupper-router pod will only be present if you have deployed an application that uses the Interconnect.
The skupper-service-controller pod will always be present whenever the skupper extension is deployed, regardless of whether or not any applications use the Interconnect.
There should be a service for each annotated service(s) in your server application.
On the server (Hub) side, the Service will be of type LoadBalancer and will have an IP address assigned.
Note
They are maintained by skupper-site-controller in the skupper-site-controller namespace. The are no CRDs associated with Skupper interconnect on the Edge cluster.