EtherCAT Master Stack#
Introduction#
The EtherCAT master stack by IgH* is used for open source projects for automation of systems such as Robot Operating System (ROS) and Linux* CNC. Applications of an open source–based EtherCAT master system reduces cost and makes application program development flexible. Based on the native, Intel® made the following optimizations:
Features#
Support Linux* Kernel 5.x/6.x
Support Xenomai* 3/dovetail and Preempt RT
Migrate latest IGB/IGC/mGBE driver to stack
Support user-mode runtime
Support multiple master
For User-space EtherCAT Master Stack, please visit Userspace EtherCAT Master Stack for details.
Architecture Overview#
The architecture is as following:
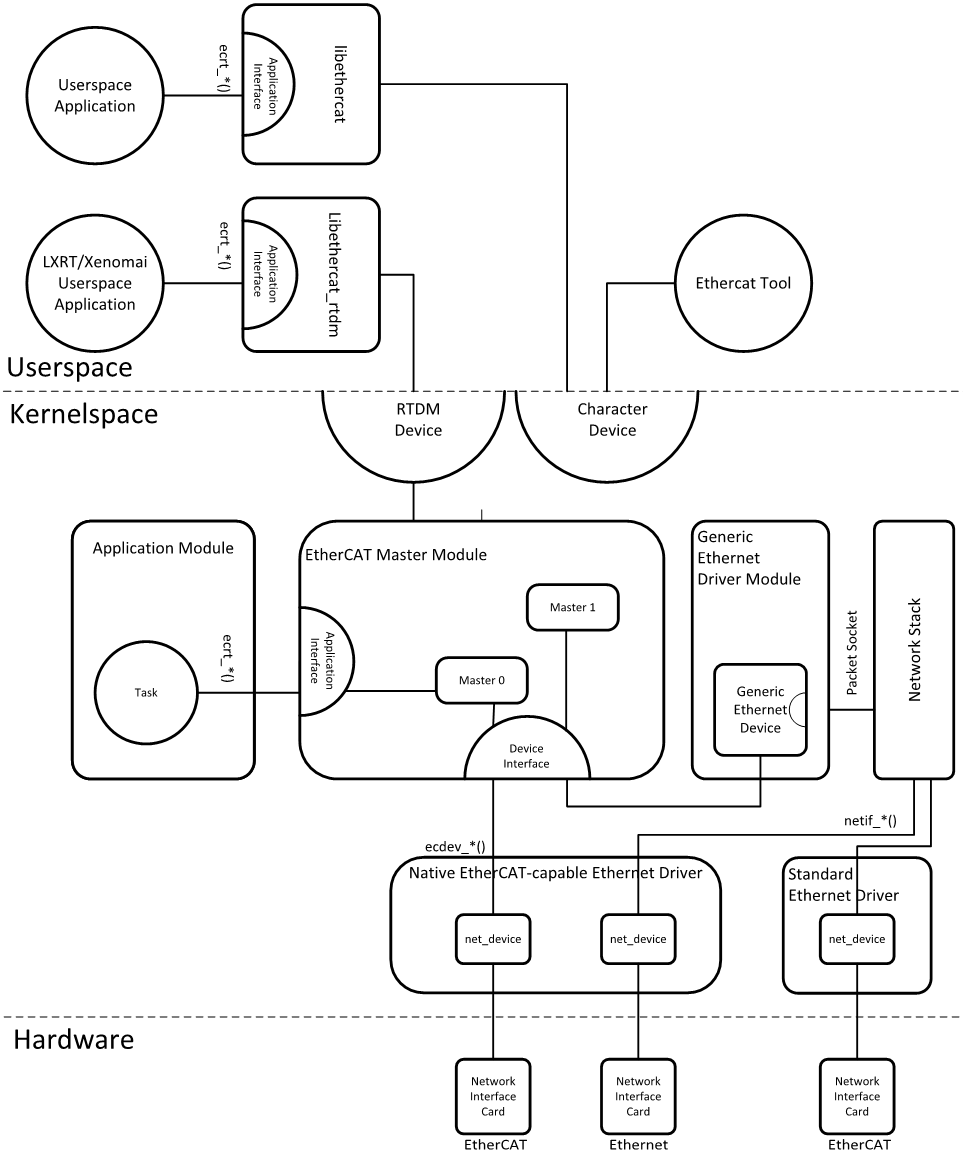
Three key blocks have been introduced to support the core architecture:
Master Module is as Kernel module containing one or more EtherCAT master instances, the ‘Device interface’ and the ‘Application Interface’.
Device Modules is EtheCAT-capable Ethernet device driver modules, that offer their devices to the EtherCAT master via the device interface. These modified network drivers can handle network devices used for EtherCAT operation and ‘normal’ Ethernet devices in parallel. A master can dedicate to access a certain device which is optimized for EtherCAT communication as device module.
Application is a program that uses the EtherCAT master (usually for cyclic exchange of process data with EtherCAT slaves). These programs are not part of the EtherCAT master code, but require to be generated or written by the user. An application can request a master through the appliation interface. If this succeeds, it has the control over the master: It can provide a bus configuration and exchange process data. Applications can be kernel modules that use the kernel application interface directly. They also include user space programs, which use the application interface via the EtherCAT library or the RTDM library.
Getting Started#
Installing Dependencies (Oneshot Time)#
Run the following packages to install dependence packages for building in Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install autoconf automake git libtool build-essential libmodbus5 libmodbus-dev
Installing Patches (Oneshot Time)#
Firstly, pull submodule locally using git:
git submodule init
git submodule update
Run the script install_etherlab_patched.sh to apply optimizated patches in ighethercat folder, the patch list is defined in patches/ighethercat.scc.
./install_ethercatlab_patched.sh patches/ighethercat.scc
Building EtherCAT Stack#
EtherCAT Master Stack includes master and device modules and support to build as out-of-tree kernel modules that are not part of the linux kenrel source tree. It requires to specific kernel source dir with --with-linux-dir to be compatible with the specific kernel version and configuration of the kernel, ensure that the module interfaces correctly with the kernel’s internal APIs and data structures.
So that, linux kernel source need to be compiled with configuation of the kernel, and use --with-linux-dir to specific kernel directory.
Recommend using environment variables kernel_source_dir to configure it.
export kernel_source_dir=<specific your linux kernel directory>
which Following with below commands to build EtherCAT Master Stack:
For Preempt-RT:
cd ighethercat
./bootstrap
./configure --enable-sii-assign --disable-8139too --disable-eoe --enable-igb --enable-igc --with-linux-dir=${kernel_source_dir} --with-devices=8 --enable-hrtimer --enable-cycles
make modules all
For Xenomai/Dovetail:
cd ighethercat
./bootstrap
./configure --enable-sii-assign --disable-8139too --disable-eoe --enable-igb --enable-igc --with-linux-dir=${kernel_source_dir} --enable-rtdm --with-xenomai-dir=/usr/include/xenomai --with-xenomai-config=/usr/bin/xeno-config --with-devices=8 --enable-hrtimer --enable-cycles
make modules all
Note: If you need DKMS to compile master and device modules, please refer to How to build EtherCAT with DKMS
Installing The Software#
The below commands have to entered as root, which will install the EtherCAT header, service scripts, kernel modules and userspace tool to the prefix path.
make install
make modules_install
depmod
Configuring EtherCAT Device#
A mandatory ethercat file installed in /etc/sysconfig/. The ethercat file contains the configuration variables needed to operate one or more masters.
Do the following to configure it:
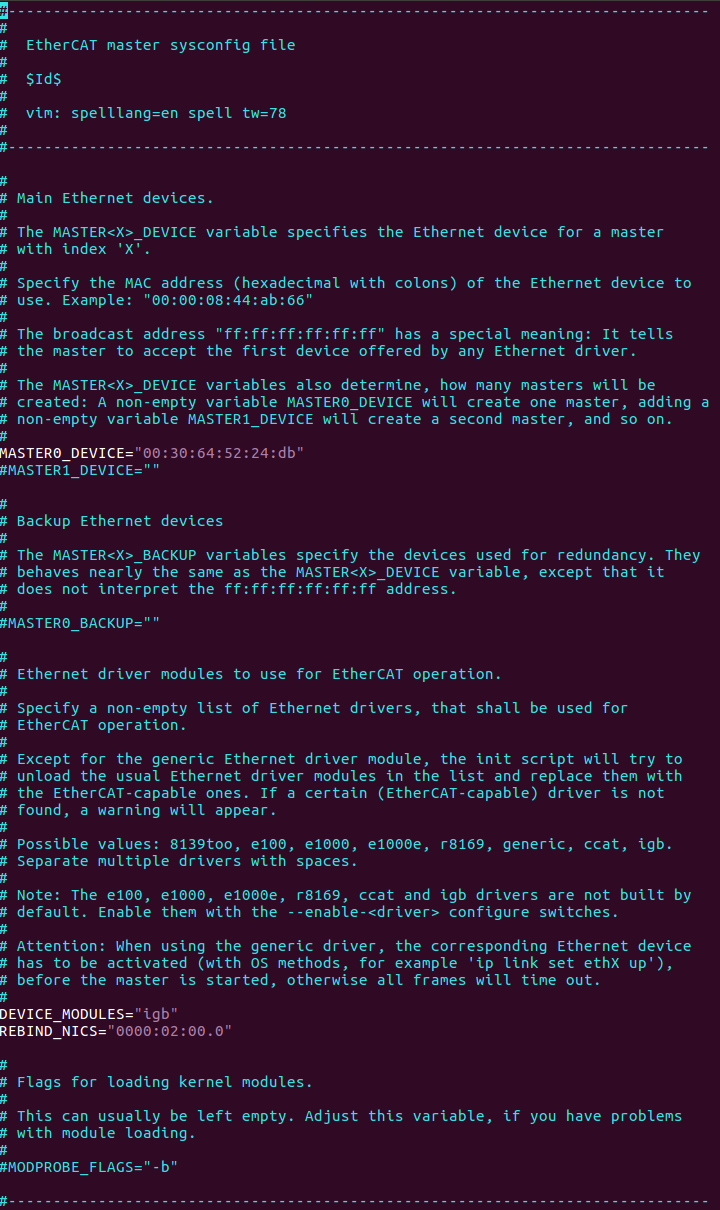
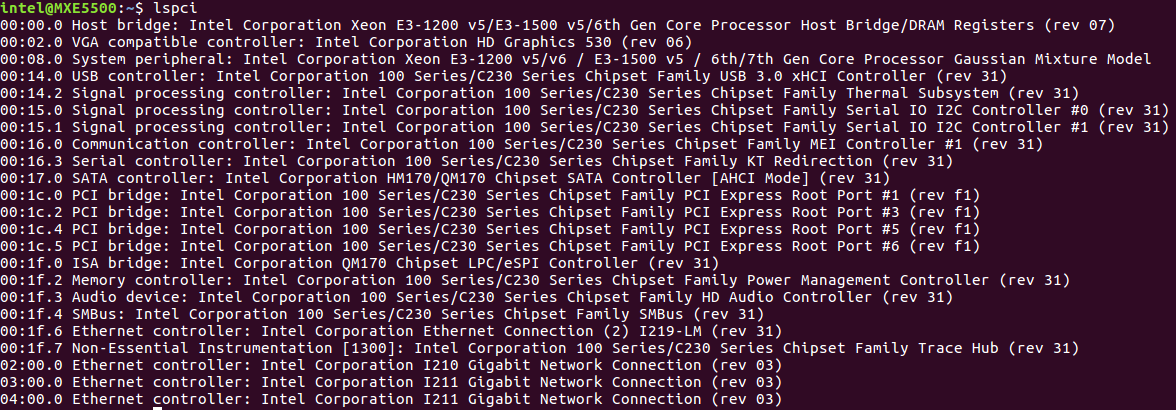
Set REBIND_NICS. Use
lspcito query net devices. One of the devices might be specified as an EtherCAT network interface.
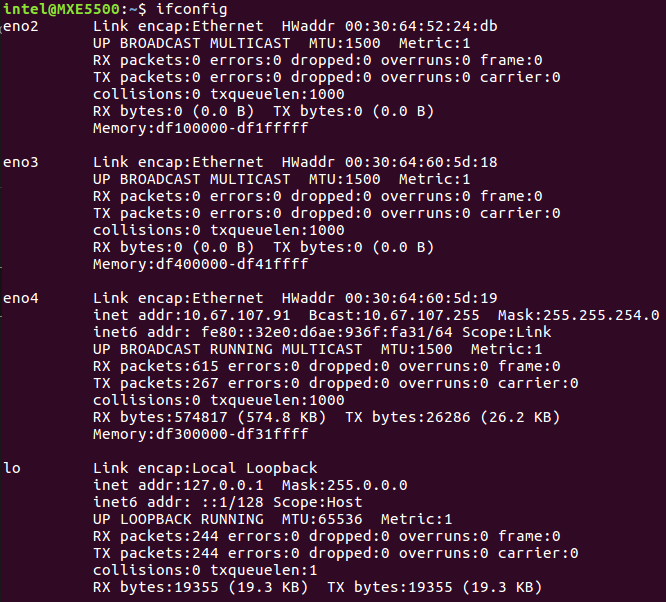
Fill the MAC address for MASTER0_DEVICE. Get the MAC address of the Network Interface Controllers (NICs) selected for EtherCAT.
Note: EtherCAT Master Stack supports dual master configuration. To configure a secondary master, fill the MAC address for MASTER1_DEVICE and add PCI address in REBIND_NICS.
Modify DEVICE_MODULES:
Option 1: Intel Corporation I210/I211 GbE controller EtherCAT driver (High performance)
DEVICE_MODULES="igb"
Option 2: Intel Corporation I225/I226 GbE controller EtherCAT driver (High performance)
DEVICE_MODULES="igc"
Option 3: Intel® Core™ 12th S-Series [Alder Lake] and 11th Gen P-Series and U-Series [Tiger Lake] Intel® Atom™ x6000 Series [Elkhart Lake] GbE controller EtherCAT driver (High performance)
DEVICE_MODULES="dwmac_intel"
Fallback: Generic driver as EtherCAT driver (Low performance)
DEVICE_MODULES="generic"
Start Master as Service#
After the init script and the sysconfig file are ready to configure, and are placed in the right location, the EtherCAT master can be inserted as a service. You can use the init script to manually start and stop the EtherCAT master. Execute the init script with one of the following parameters:
Operation |
Command |
|---|---|
Start EtherCAT Master |
|
Stop EtherCAT Master |
|
Restart EtherCAT Master |
|
Status of EtherCAT Master |
|
Makefile Template for EtherCAT application#
Provided below are some Makefile templates for EtherCAT application. These templates are provided to build EtherCAT application without Makefile.am.
Makefile template for Preempt-RT kernel
CC = gcc
CFLAGS = -Wall -O3 -g -D_GNU_SOURCE -D_REENTRANT -fasynchronous-unwind-tables
LIBS = -lm -lrt -lpthread -lethercat -Wl,--no-as-needed -L/usr/lib
TARGET = test
SRCS = $(wildcard *.c)
OBJS = $(SRCS:.c=.o)
$(TARGET):$(OBJS)
$(CC) -o $@ $^ $(LIBS)
clean:
rm -rf $(TARGET) $(OBJS)
%.o:%.c
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o $@ -c $<
Makefile template for Xenomai/Dovetail kernel
CC = gcc
CFLAGS = -Wall -O3 -g -I/usr/include/xenomai/cobalt -I/usr/include/xenomai -D_GNU_SOURCE -D_REENTRANT -fasynchronous-unwind-tables -D__COBALT__ -D__COBALT_WRAP__
LIBS = -lm -lrt -lpthread -lethercat_rtdm -Wl,--no-as-needed -Wl,@/usr/lib/cobalt.wrappers -Wl,@/usr/lib/modechk.wrappers /usr/lib/xenomai/bootstrap.o -Wl,--wrap=main -Wl,--dynamic-list=/usr/lib/dynlist.ld -L/usr/lib -lcobalt -lmodechk
TARGET = test
SRCS = $(wildcard *.c)
OBJS = $(SRCS:.c=.o)
$(TARGET):$(OBJS)
$(CC) -o $@ $^ $(LIBS)
clean:
rm -rf $(TARGET) $(OBJS)
%.o:%.c
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o $@ -c $<
License#
The source code is licensed under the GPL v2. See COPYING file for details. To allow dynamic linking of userspace application against the master’s application interface, the userspace library is licensed under the LGPL v2.1. See COPYING.LESSER