Robot Motion Control Task#
Overview#
Robotmctask is a comprehensive C++ library designed for robot motion control task development. It provides APIs that enable robot developers to build sophisticated robot applications with integrated AI inference engines and EtherCAT protocol support.
Key Features:#
PLCOpen Compliance: Support for PLCOpen motion control function blocks
Multi-Task Support: Concurrent handling of multiple motion control tasks
Real-Time Integration: Seamless shared memory communication between real-time and non-real-time domains
AI-Powered Control: Built-in inference engine support for intelligent motion control
Simulation Ready: Comprehensive motion control simulation capabilities
Architecture Overview#
The architecture is as following:

Two key blocks have been introduced to support the core architecture:
libectask is a dynamic library that provides a set of public APIs for EtherCAT real-time task creation. Key capabilities include:
EtherCAT Integration: Creates motion function blocks to operate EtherCAT slaves using ENI configurations
Network Topology Support: Handles slave configurations and network topology definitions
Flexible Memory Management: Supports custom shared memory callbacks for data restructuring between real-time and non-real-time domains
AI Pipeline Integration: Enables AI inference callback registration within real-time tasks, facilitating seamless AI model integration into motion control workflows, and supports running inference on NPU device within real-time constraints.
libinference is a shared library offering advanced inference capabilities with:
Modern C++ Interface: New C++ classes for streamlined inference implementation
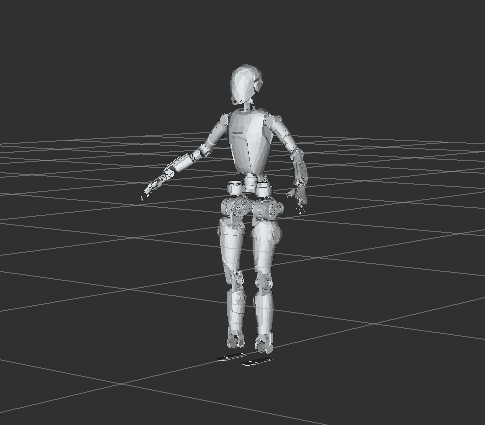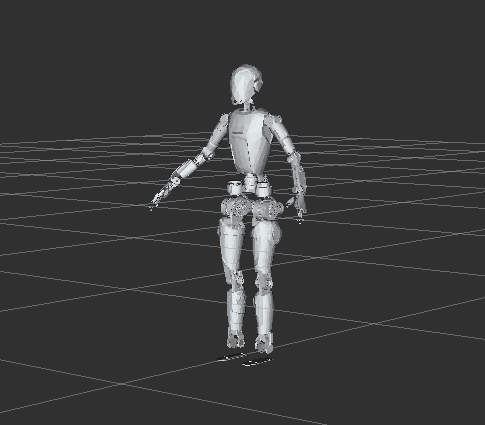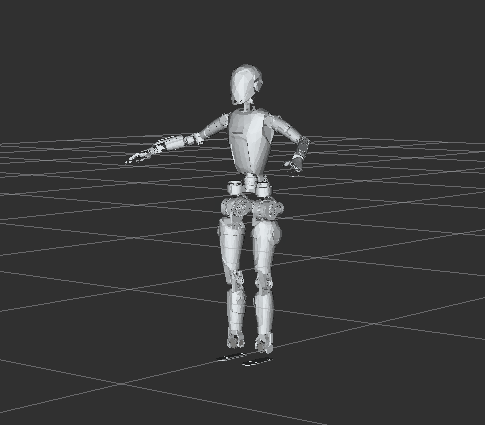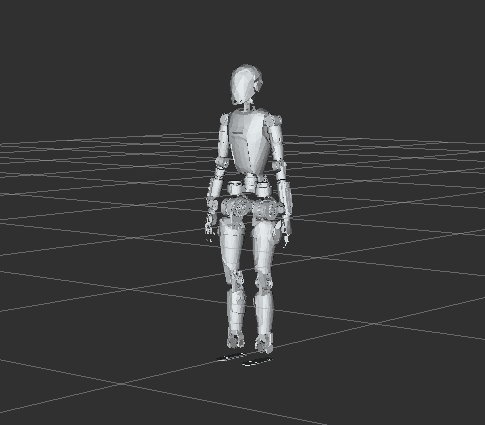
Reinforcement Learning Support: Integrated RL classes optimized for robotic applications. To facilitate quick demonstrations of code functionality, provides a stable-standing ONNX model based on real robot, running inference on an NPU device. This model maintains whole-body balance by controlling the lower limbs while the upper body performs hand movements. Such a model enables humanoid robots to remain stable through reinforcement learning when the upper limbs are engaged in VLA tasks.
Performance Analytics: Built-in statistical collection for performance monitoring
Intel OpenVINO integration: Default inference engine with extensible architecture
Extensible Design: Bases classes enabling custom AI model development
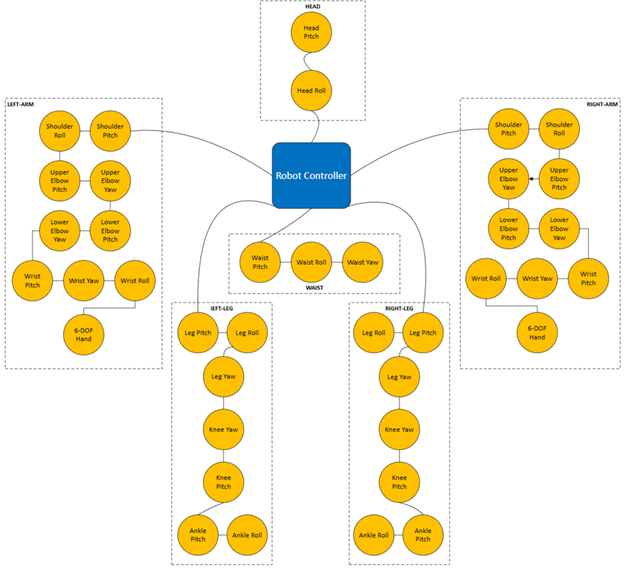
Network Topology#
The following diagram illustrates a typical fieldbus topology for humanoid robot applications:
Getting Started#
Requirements#
The software runs on standard PCs or servers. Since it is primarily developed in C++, porting to other operating systems is straightforward.
Running#
Please check README file for details.
Examples#
One example using Robot Motion Control Task is provided.
mc_rl_sample: A comprehensive demonstration showcasing:
Multi-Topology Configuration: Robot task setup with multiple topologies using different ENI files
Distributed Control: Three separate ectasks controlling distinct EtherCAT topologies:
Left/Right Arm Control
Leg control systems
Dual Arm Integration: Joint state publishing via shared memory for VLA(Vision-Language-Action) models or simulator integration
Custom Motion Algorithms: Leg control with registered callbacks for customized motion algorithms and inference pipelines
License#
The source code is licensed under Apache License . See LICENSE file for details.