iRobot Create 3#
iRobot Create 3 is a mobile robotics platform, which developers can use to gain hands-on experience with the technologies and concepts that are foundational to the field of autonomous mobile robots. This practical understanding is invaluable for those looking to enter the robotics industry or further their knowledge in this rapidly evolving field.
Before starting, review the iRobot Create 3 mobile robotics platform documentation to be able to perform the configuration changes needed for the tutorial.
iRobot Create 3 hardware extensions#
iRobot Create 3 contains a compute unit running ROS 2 that provides access to the on-board sensors and actuators. For this tutorial, the following modifications have been applied to the robot:
two support layers added on top of the robot,
Intel® board mounted on the bottom layer,
Intel® RealSense™ camera mounted on the front of the top layer and connected to a USB port on the Intel® board,
Slamtec RPLIDAR 2D (Slamtec RPLIDAR A3 laser range scanner or Slamtec RPLIDAR A2 laser range scanner (A2M8)) sensor on a mount in the center of the top layer and connected to two USB ports on the Intel® board,
custom battery in the cargo bay to power the Intel® board and accessories, namely the camera and the lidar,
an Ethernet adapter connected to the iRobot Create 3 adapter board and to the Intel® board,
a rear caster wheel attached to the cargo bay, as described in the iRobot® Create® 3 Mechanical System documentation.
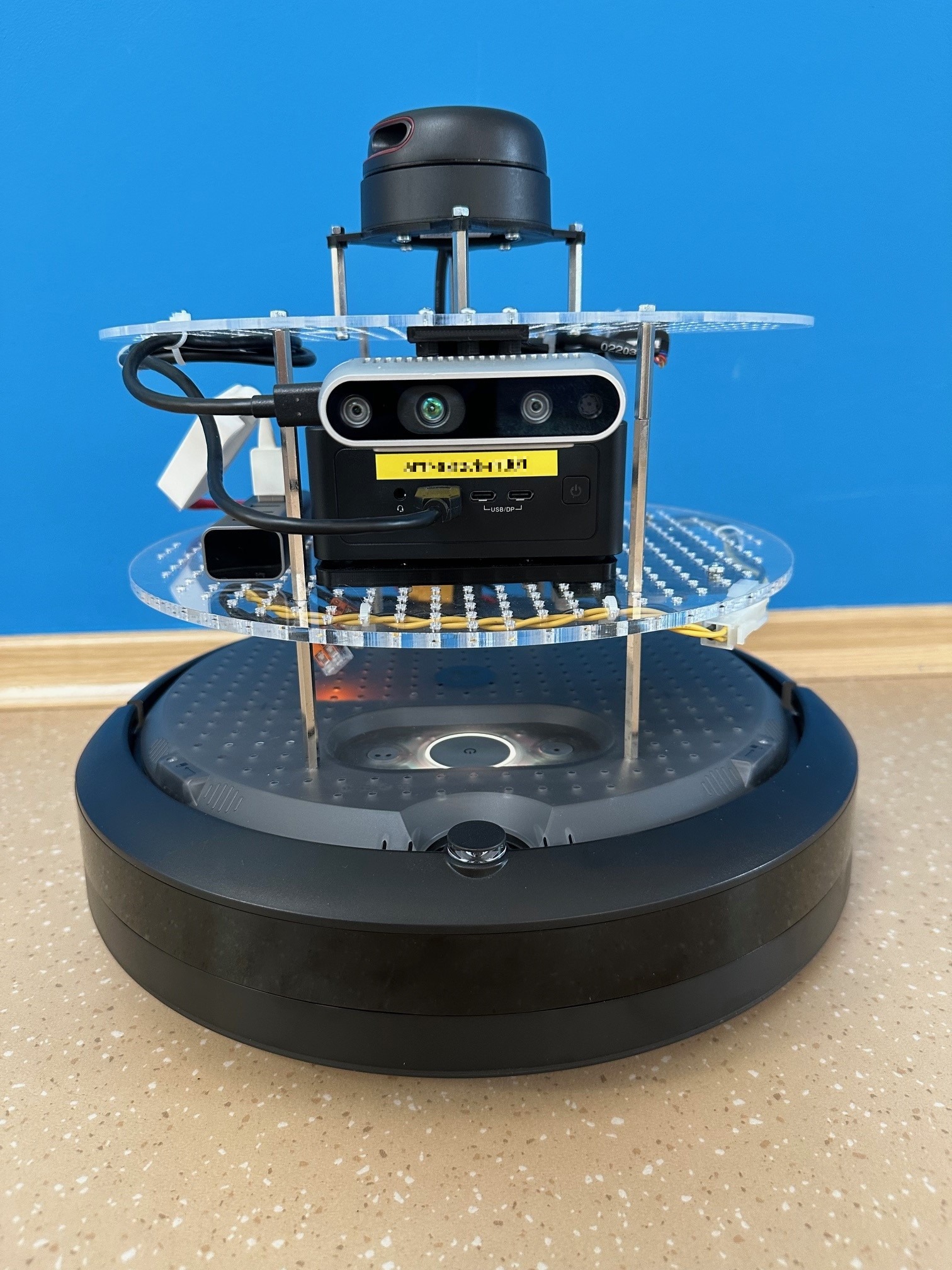

iRobot Create 3 robot front view.#
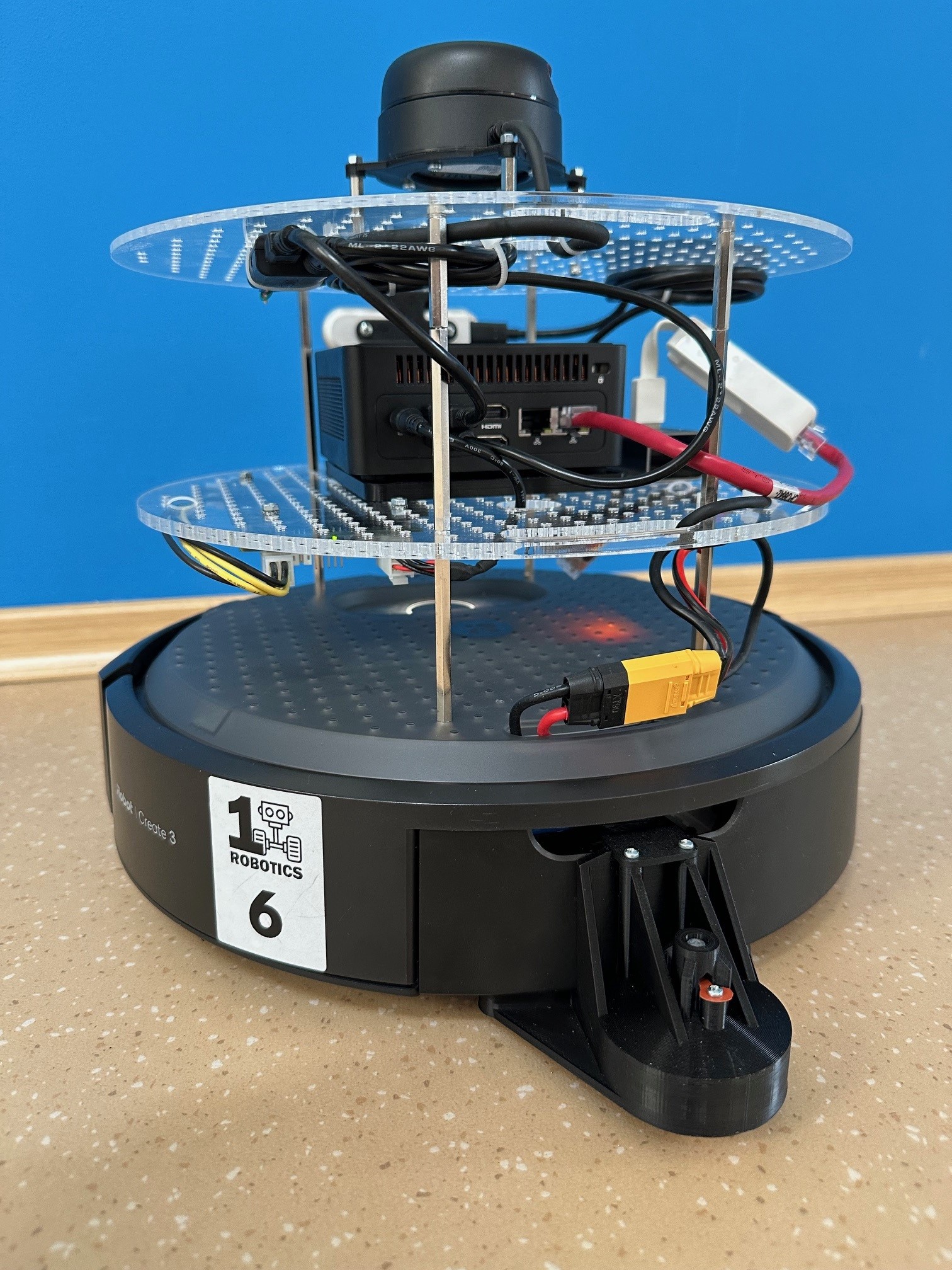

iRobot Create 3 robot rear view.#
iRobot Create 3 software configuration#
Update the robot to use the latest ROS 2 Humble firmware and configure it to access your WiFi network following the iRobot® Create® 3 Setup documentation.
With the robot connected to your WiFi network continue configuring it using its web interface. Refer to the iRobot Create 3 mobile robotics platform documentation for the exact steps to follow.
Wired (Ethernet) network#
The Intel® board and the compute unit of the iRobot Create 3 should be connected using an Ethernet adapter with a USB Type-C connector. The USB Type-C plug should be connected to the adapter board of the iRobot Create 3, while the Intel® board should be connected to the Ethernet adapter using an RJ-45 cable.
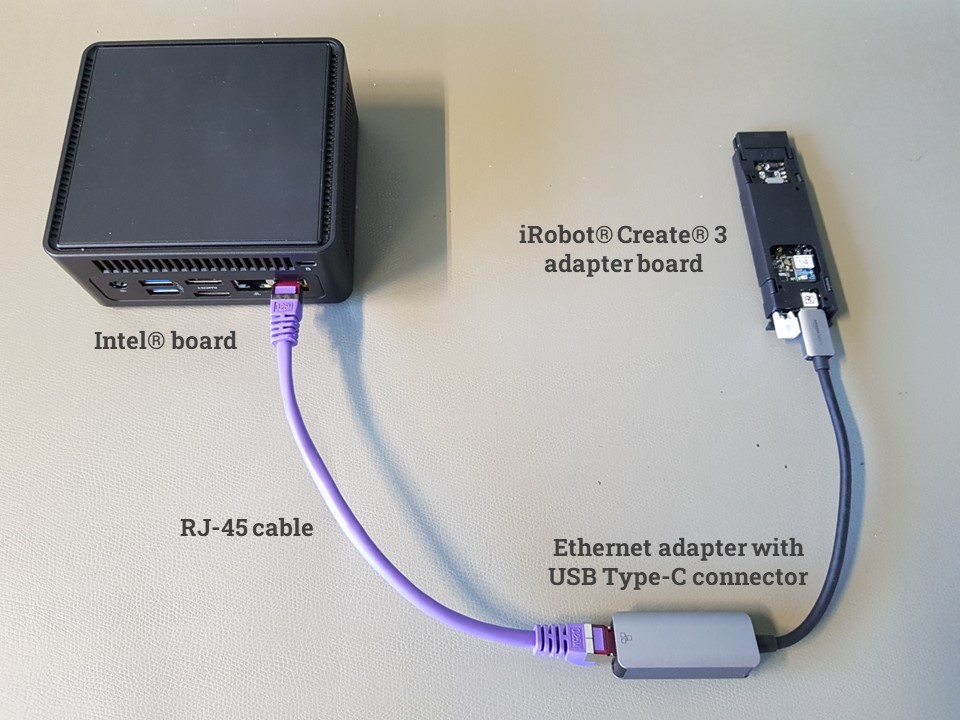
Ethernet via USB connection between iRobot Create 3 adapter board and Intel® board.#
The iRobot Create 3 robot is configured to use the address
192.168.186.2/24 on the USB interface. You can change the network
part of the address by following the instructions on page
iRobot Create 3 Webserver - Set Wired Subnet.
On the Intel® board, the network interface connected to the robot has to be configured with a static IP address of the same subnet.
NTP server#
Time synchronization is very important in ROS 2. For this reason, the iRobot Create 3 includes an NTP server, which can be configured as described on page iRobot® Create® 3 Webserver - Edit ntp.conf.
Alternatively, you can set up an NTP server on the Intel® board by following the iRobot Create 3 documentation Set up NTP on compute board. Use the IP address of the Ethernet interface connected to the robot.
ROS 2 Middleware (RMW) Configuration & Fast DDS discovery server#
To define what ROS 2 middleware implementation shall be used by the
iRobot Create 3, follow the configuration guidelines on page
iRobot Create 3 Webserver - Application.
Set the RMW_IMPLEMENTATION option to rmw_fastrtps_cpp, as shown in
the figure below.
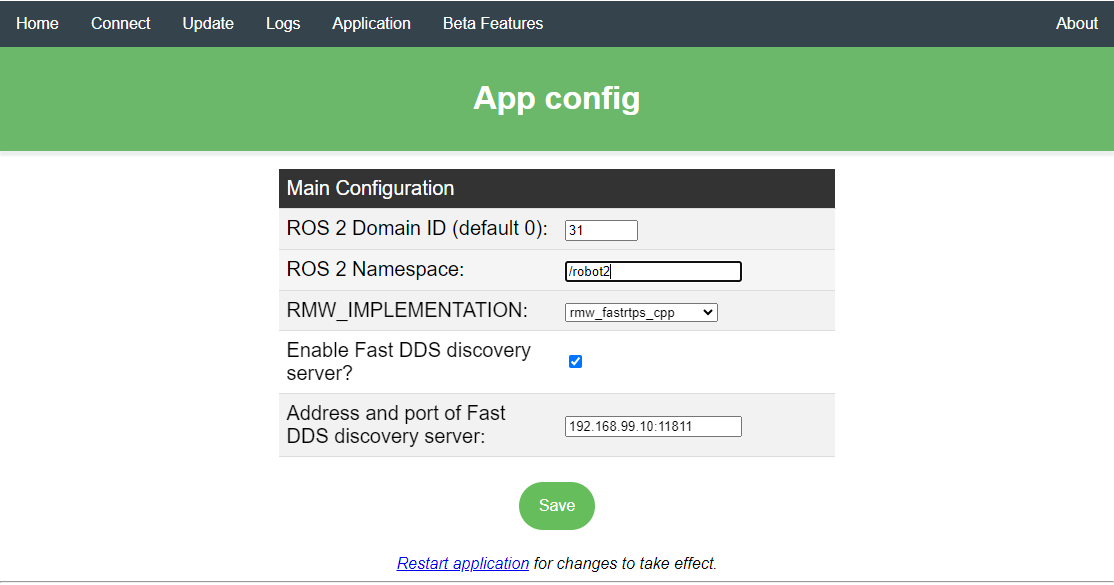
iRobot Create 3 ROS 2 Humble application configuration page. On this
robot the iRobot Create 3 Webserver - Set Wired Subnet
is set to 192.168.99.2, Fast DDS discovery server is enabled
and runs on the Intel® board reachable at IP 192.168.99.10
over the Ethernet connection. ROS 2 Domain ID is set but it is not
used when the discovery server is enabled.#
To speed up node discovery, enable the iRobot® Create® 3 Fast DDS Discovery Server. Use the IP address set above for the Intel® board on the USB connection to the iRobot Create 3 as the Fast DDS Discovery Server IP address.
Note
When the discovery server is enabled, the ROS_DOMAIN_ID is not used.
Robot namespace#
Set a ROS 2 namespace (e.g., /robot2) for your robot, as described on page
iRobot Create 3 Webserver - Application. This value should be passed to the
launch file as argument irobot_ns.
iRobot Create 3 Wandering tutorial#
This tutorial presents the Wandering application running on an iRobot Create 3 mobile robotics platform extended with an Intel® compute board, an Intel® RealSense™ camera and a Slamtec RPLIDAR 2D lidar sensor.
The tutorial uses the Intel® RealSense™ camera and the Slamtec RPLIDAR 2D lidar sensor for both mapping with RTAB-Map and navigation with Nav2. For navigation, Intel® ground floor segmentation is used for segmenting ground level and remove it from the Intel® RealSense™ camera pointcloud.
Watch the video for a demonstration of the iRobot Create 3 navigating in a testing playground:
Intel® board connected to iRobot Create 3#
Follow the instructions on page iRobot® Create® 3 - Network Recommendations to set up an Ethernet over USB connection and to configure the network device on the Intel® board. Use an IP address of the same subnet as used on the iRobot Create 3.
Check that the iRobot Create 3 is reachable over the Ethernet connection. Output on the robot with the configuration from the image above:
$ ping -c 3 192.168.99.2
PING 192.168.99.2 (192.168.99.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.99.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.99 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.99.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=2.31 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.99.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=2.02 ms
--- 192.168.99.2 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2004ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 1.989/2.105/2.308/0.144 ms
Install the ros-humble-wandering-irobot-tutorial package on the
Intel® board connected to the robot.
apt install ros-humble-wandering-irobot-tutorial
Start the discovery server in a new terminal:
fastdds discovery --server-id 0
In a new terminal set the environment variables for ROS 2 to use the discovery server:
export ROS_DISCOVERY_SERVER=127.0.0.1:11811
export ROS_SUPER_CLIENT=true
unset ROS_DOMAIN_ID
Check that the setup is correct by listing the ROS 2 topics provided by the robot:
ros2 topic list
The iRobot Create 3 topics should be listed:
/parameter_events
/robot2/battery_state
/robot2/cliff_intensity
/robot2/cmd_audio
/robot2/cmd_lightring
/robot2/cmd_vel
...
/robot2/tf
/robot2/tf_static
/robot2/wheel_status
/robot2/wheel_ticks
/robot2/wheel_vels
/rosout
Note
If only /parameter_events and /rosout topics are listed then
the communication between the robot and the Intel® board is not
working. Check the iRobot Create 3 mobile robotics platform documentation to troubleshoot
the issue.
Start the tutorial using its launch file; provide the namespace set on
the robot in the argument irobot_ns:
ros2 launch wandering_irobot_tutorial wandering_irobot.launch.py irobot_ns:=/robot2
To use ros2 cli utilities, e.g. ros2 topic, ros2 node, set the
environment variables above before running the commands.