Argo* CD Architecture#
Background#
Argo* CD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes*. It is a CNCF graduated project used by hundreds of large enterprises to manage their Kubernetes* applications. Argo CD automates the deployment of the desired application states in the specified target environments. By using Git as the source of truth for application definitions, configurations, and environments, Argo CD ensures that the state of applications is always consistent and reproducible.
Open Edge Platform chooses Argo CD as the continuous delivery tool for Edge Orchestrator deployments*.
Target Audience#
Solution Architect who would like to understand software lifecycle management of Edge Orchestrator.
Operator who would like to deploy Edge Orchestrator.
Concepts#
For detailed concepts and terminologies, refer to the official Argo CD documentation .
Overview#
Both cloud and on-premises Edge Orchestrator deployments follow the same GitOps workflow as follows:
edge-manageability-framework
There is one Argo CD instance and one Gitea instance deployed in each Edge Orchestrator cluster.
During initial deployment, the cloud or on-premises installer
instantiates
edge-manageability-frameworkrepository in Gitea with a snapshot captured from upstream as the initial commit.prompts user to input cluster-specific configurations (such as domain name), generate a cluster configuration in the
orch-configs/clusterssubdirectory, and deploy the Edge Orchestrator applications using Argo CD referencing the cluster configuration for deployment settings.
Argo CD is set to track the
mainbranch of the Giteaedge-manageability-frameworkrepository by default. (can be changed if desired)
In the following sections, we will explain how we design our GitOps repo to minimize configuration duplication and inconsistency across Edge Orchestrator instances. We will also go over the development workflow and provide a few troubleshooting tips.
Architecture Diagram#
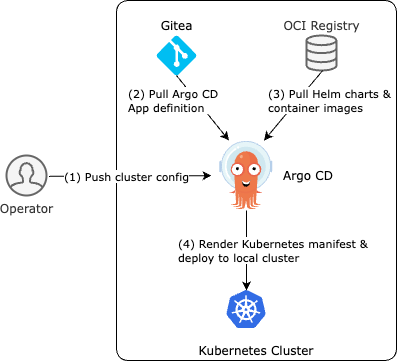
Figure 1: Argo CD in Edge Orchestrator#
Operator defines cluster-specific parameters and pushes the information to Argo CD.
Argo CD fetches the Application definition from the GitOps repository, combining it with the cluster-specific parameters from step 1, and renders the Argo CD Application CR.
Argo CD pulls Helm charts and container images from the OCI registry according to the Application CR.
Argo CD renders the final Kubernetes manifest of each application, and applies it to the cluster.
Key Components#
The Edge Orchestrator deployment only requires the
edge-manageability-framework repository.
edge-manageability-framework repository#
open-edge-platform/edge-manageability-framework
Root App definition
Root App is a special Argo CD Application that is used to bootstrap a cluster. It loads cluster-specific configuration and renders the rest of the Argo CD Applications.
Argo CD Applications
Definition for each Edge Orchestrator service. For example, chart URL, chart version.
Helm* template for cluster-specific values
for example, cluster name, domain name.
Installers
Cloud installer (including Terraform scripts) and on-premises installer
Virtual Integration Pipeline (VIP) tests
The repo structure is outlined as follows, last updated on Apr 16, 2025. It is subject to minor adjustments and omits less important files.
.
├── argocd
│ ├── applications
│ │ ├── configs # General Orchestrator application settings
│ │ ├── custom # Templates used to provide cluster specific
│ │ ├ # settings.
│ │ ├── templates # Orchestrator application definitions
│ └── root-app
│ ├── templates
│ │ └── root-app.yaml # Root app used to bootstrap deployment
├── argocd-internal # Virtual edge node (development/testing)
├── bootstrap # Configuration required to bootstrap the deployment
├── e2e-tests # CI/CD Tests
├── installer # Cloud installer container
├── mage # Development deployment and test ops implementation
├── node # Virtual edge node (development/testing)
├── on-prem-installers # On-prem installer implementation
├── orch-configs
│ ├── clusters # Cluster configurations
│ ├── profiles # Profiles referenced by Cluster configurations to
│ ├ # provide blocks of configuration based on target
│ ├ # cluster environment and major component options.
│ └── templates # Templates for generating cluster and platform
│ └ # service configuration
├── pod-configs # Cloud infrastructure Terraform definitions
├── tools # Miscellaneous tools used to support developement
| # and CI/CD workflows
└── README.md # Something you should always read first :)
orch-utils repository#
This repo hosts utility charts that facilitate the deployment. For example, pre-install and post-install hooks are packaged as small Helm charts that launch Kubernetes jobs. Deployment order is enforced using Argo CD sync wave.
This repo also hosts Go code and Dockerfile of various deployment tools such
as secrets-config used to bootstrap the Edge Orchestrator Vault instance.
These utility charts are generally used by the Edge Orchestrator deployment using published production versions available from the Edge Orchestrator OCI server. It is possible to use local development versions of these charts for testing purposes.
The repo structure is outlined as follows, last updated on Apr 16, 2025. It is subject to minor adjustments and omits less important files.
IAM incoming.
.
├── charts # Pre/post-install tasks, implemented as K8s jobs
├── keycloak-tenant-controller # Multi-tenancy Keycloak integration
├── mage # Development deployment and test ops implementation
├── Makefile # Makefile for standardized build wrappers for Mage targets
├── nexus # Multi-tenancy library
├── nexus-api-gw # Multi-tenancy API gateway
├── README.md # Something you should always read first :)
├── squid-proxy # Squid Proxy for EN connection forwarding
├── tenancy-api-mapping # Multi-tenancy API
├── tenancy-datamodel # Multi-tenancy data model
├── tenancy-manager # Multi-tenancy manager
├── tools # Miscellaneous tools such as YAML lint config
├── traefik-plugins # Plugins for Traefik ingress
Data Flow#
Our Argo CD repo structure is designed in a way to minimize config duplication
and inconsistency across multiple environments. We can see the following
configs in any template in edge-manageability-framework:argocd/applications/templates:
spec:
sources:
- helm:
valueFiles:
- '$values/argocd/configs/{{$appName}}.yaml'
valuesObject:
{{- $customFile := printf "custom/%s.tpl" $appName }}
{{- $customConfig := tpl (.Files.Get $customFile) . | fromYaml }}
{{- $baseFile := printf "configs/%s.yaml" $appName }}
{{- $baseConfig := .Files.Get $baseFile|fromYaml}}
{{- $overwrite := (get .Values.postCustomTemplateOverwrite $appName )
| default dict }}
{{- mergeOverwrite $baseConfig $customConfig $overwrite | toYaml |
nindent 10 }}
There are 3 types of Helm values defined here:
(1) Base values -
edge-manageability-framework:argocd/applications/configs/{appName}.yamlThis is the common, static values shared across clusters/environments.
No template. Just static values.
Covers ~80% of the values.
(2) Custom values -
edge-manageability-framework:/argocd/applications/custom/{appName}.tplThis is cluster/environment-specific values generated from a Helm template.
We leverage Helm template such that we can minimize the footprint.
Helm value comes from cluster config provided by operator during deployment.
Covers ~20% of the values.
(3) Overwrite values - cluster config, in the
postCustomTemplateOverwritesectionThis is an arbitrary, raw YAML value.
Only use it as a last resort when we need to overwrite something that has not been defined in the
customtemplate yet.It is intended for hotfix and troubleshooting, not for long-term use.
The guideline is to put as much as possible in (1) and (2), and only use (3) for short-term, troubleshooting purposes.
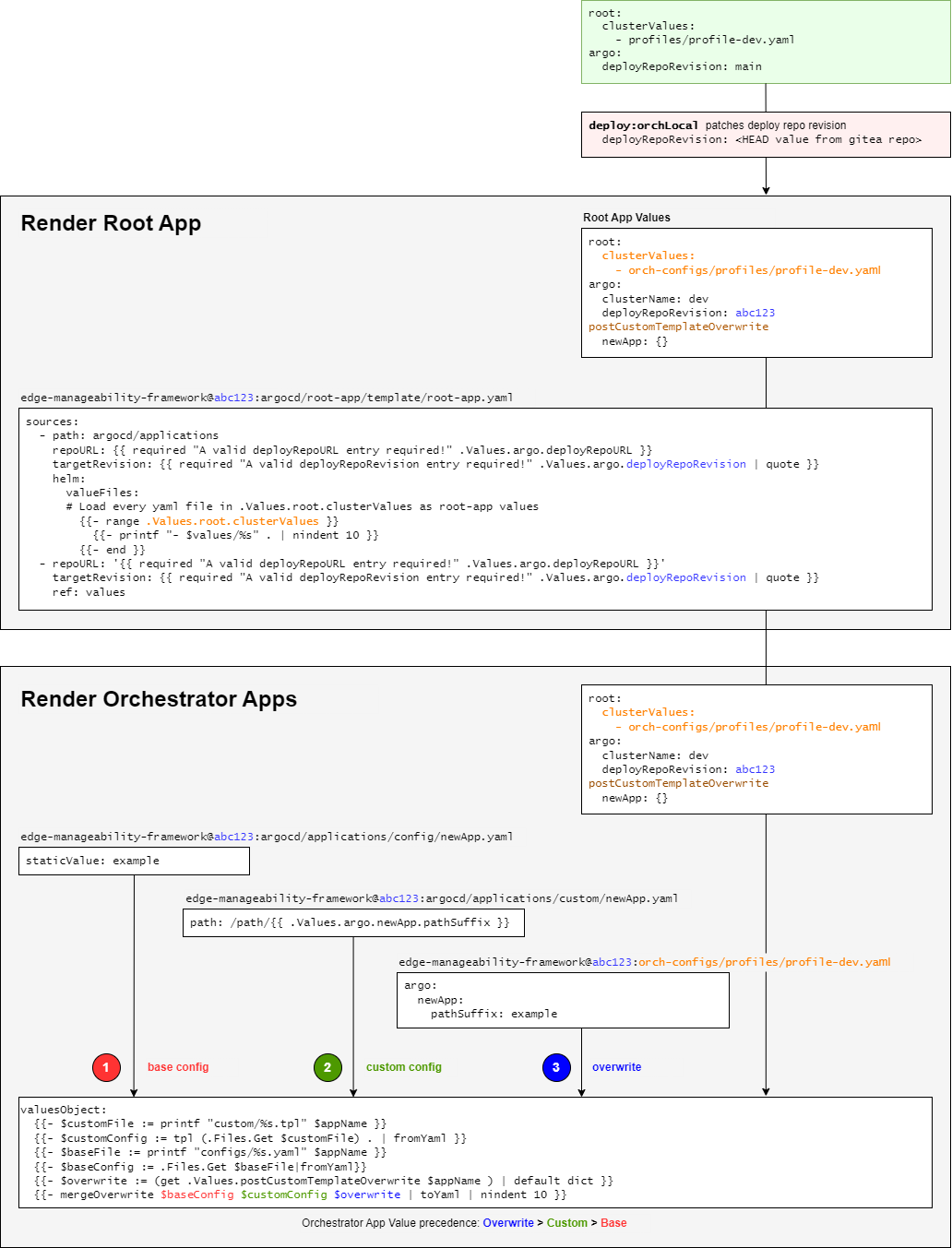
Figure 2: Argo CD configuration flow#
Note that the Helm values passed to the root app during deployment only apply to the root app.
The root app can then decide whether it wants to further pass these values down to Edge Orchestrator Argo CD applications or not.
We implemented a Helm value in the root app to support both behaviors.
The root app will pass these values to the child app when
.Values.root.useLocalValuesis set to true.Otherwise, the child app will use the version of values defined in the remote orch-configs repo.
Workflow Stages#
Refer to the description in the Architecture Diagram section.
Extensibility#
This section explains the workflow of modifying existing or introducing new Argo CD applications for Edge Orchestrator. This is typically done after you have developed your change in one of the Edge Orchestrator components. Refer to Edge Orchestrator component development guide at:
Make changes#
Application Definition#
This is located at
edge-manageability-framework:argocd/applications/templates/{appName}.yaml.
Base Value#
This is located at /argocd/applications/configs/{appName}.yaml.
These values generally come from the default values.yaml file associated
with the application Helm chart.
Custom Template#
This is located at /argocd/applications/custom/{appName}.tpl
These are values that will need to be specified based on some deployment target specific value such as the domain name of the target cluster. This usually requires some effort in taking the specific values and creating a template that will render those values based on settings that will be defined by the cluster definition for each deployment target.
Custom Value and feature flag#
This is located at /orch-configs/clusters/{env}.yaml and
/orch-configs/profiles/*.yaml
We need to make sure the values for the aforementioned custom template are listed in either:
For cluster-specific values, list them directly in
orch-configs:clusters/{env}.yamlFor values shared among multiple clusters with similar characteristics, list them in
/orch-configs/profiles/*.yamland refer to the profile in the.Values.root.clusterValuessection of the/orch-configs/clusters/{env}.yaml
Regardless of whether a value is cluster-specific or referred to as a profile
Common values shared across multiple applications should be defined under
.Values.argo.For example,
.Values.argo.clusterDomain
Values specific to one or a small set of applications should be defined under
.Values.argo.{appName}.For example,
.Values.argo.database.type
We also need to implement the feature flag that allows us to toggle individual components.
This should go into the
.Values.argo.enabled.{appName}section in the corresponding/orch-configs/profiles/enable-*.yamlFor example,
.Values.argo.enabled.infra-coreinorch-configs:profiles/enable-edgeinfra.yaml
Overwrite Value (optional)#
It is totally optional and should only be applied for short-term use. We allow
passing arbitrary YAML to overwrite both base and custom values. This can be
done by creating a file under /orch-configs/clusters/{env}.yaml. The
content of the value should be put under
postCustomTemplateOverwrite.{appName}. For example:
postCustomTemplateOverwrite:
infra-onboarding:
# Anything here will be applied without template expansion
Contribution & Review Guidelines#
Note
Please read this section thoroughly so we can ensure a delightful and efficient review process for both contributors and reviewers.
Common guidelines#
Refer to Contributing for common development guidelines.
edge-manageability-framework guidelines#
Keep application definition (
argocd/applications/templates) as consistent as possible.Need to have strong justification for any difference, such as when adding an
ignoreDifferenceblock.
Minimize config duplication.
No need to specify values in base config if it is already defined in custom template.
Make sure any development or local test related changes to
repoURLandtargetRevisionare reverted before submitting a PR.
orch-utils guidelines#
Use official images for the pre/post-installation job as much as possible.
Test and submit updates to Edge Orchestrator components#
Make desired changes to the to the Orchestrator component application file in
edge-manageability-framework:argocd/applications/templates/{appName}.yaml.Any required changes to component settings in the
edge-manageability-framework:argocd/applications/configs/{appName}.yamloredge-manageability-framework:argocd/applications/custom/{appName}.tplshould also be applied locally.
Use the following commands to test your changes locally:
mage deploy:orchLocal [targetEnv]
This will push local changes to the
gitearepo hosted in the local Kind cluster.Call Argo CD to update the Orchestrator deployment in the local Kind cluster.
The
targetEnvvalue is the name of the cluster configuration file (orch-configs/clusters/{targetEnv}.yaml).
Deployment#
Please refer to the following pages:
Technology Stack#
Edge Orchestrator leverages open source Argo CD without modification. Please refer to the official Argo CD documentation for detailed explanation of its technology stack.
Security#
Please refer to Argo CD Security for detailed security information.
Authentication#
We generate a random admin password when Argo CD is first deployed. The admin
username is admin, and its credential can be retrieved from the Argo CD
secret as follows:
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o yaml | yq .data.password | base64 -d
Access Control#
Argo CD uses a role-based access control (RBAC) system to manage user access.
Note that we only create a local account for Argo CD. It is not connected to Keycloak*, which is the identity provider used for most of the Edge Orchestrator. There is only one “admin” account by default, and should only be accessible by the operator of Edge Orchestrator. Additional local accounts can be created on-demand.
For detailed access control configurations, refer to RBAC configuration .
Auditing#
For detailed auditing information, refer to Auditing.
Scalability#
For detailed scalability information, refer to High Availability and Reconcile Optimization.