Data Model#
The Application Orchestration data model is composed of the following parts:
Applications#
Applications are individually deployable and based on Helm* Charts and Container (Docker*) Images. They may be either container-based, or virtual machine based. The customer may leverage Application Orchestration’s internal registry to house these Helm Charts and Images, or they may leverage an external registry, such as a public registry or a private enterprise registry. Applications include named Profiles that allow the applications to be configured in different ways at deployment time.
Additionally, the profile can have a set of parameter templates that can be used to override the values in the Helm Chart at deploy time.
The purpose of the application abstraction is to be able to hide the complexity of the Helm Chart and its configuration values from the persona that will be performing the deployment, while still permitting the flexibility of configuring the application.
Extensions are a set of pre-curated applications that are provided by the Edge Orchestrator team. They are loaded on creation of a Multi-Tenancy project. Some are installed automatically on the Edge Node (those in the Cluster Base Extensions Deployment Package), and others are part of the Application Extensions Deployment Packages that can be installed by end users on demand. They usually include utility packages such as cert-manager, observability etc.
Other end-user Applications will be designed and added by end users.
Deployment Packages#
Deployment Packages are collections of Applications that may be deployed as an aggregate to an edge site. As such, a Deployment reflects a set of related Helm Charts. A Deployment Package that contains only a single Application (and therefore only reflects a single Helm Chart) is allowed. Deployment Packages extend the profile abstraction, allowing the entire collection of applications to be configured by a single profile, further simplifying the deployment process.
Deployment Package Extensions are a special case of Deployment Packages that are pre-curated and provided by the Edge Orchestrator team. In general, only one instance of an extension is deployed to an edge node cluster. They are divided into two sets - Cluster Extensions and Application Extensions.
Cluster Base Extensions Deployment Package#
Cluster Base Extensions Deployment Package are a set of pre-curated Extension Applications that extend the basic Kubernetes deployment on the Edge Node cluster to provide enhanced operational capabilities like Gatekeeper, Prometheus, Fluent Bit, OpenEBS, and others. These Deployment Packages are deployed by default on every Edge Node cluster.
Application Extensions Deployment Packages#
Application Extensions Deployment Packages are a set of pre-curated Deployment Packages loaded onto Edge Orchestrator by default that group Application Extensions. These are deployed on demand by the user to provide access to commonly used utility services like Loadbalancer, GPU support, SRIOV support.
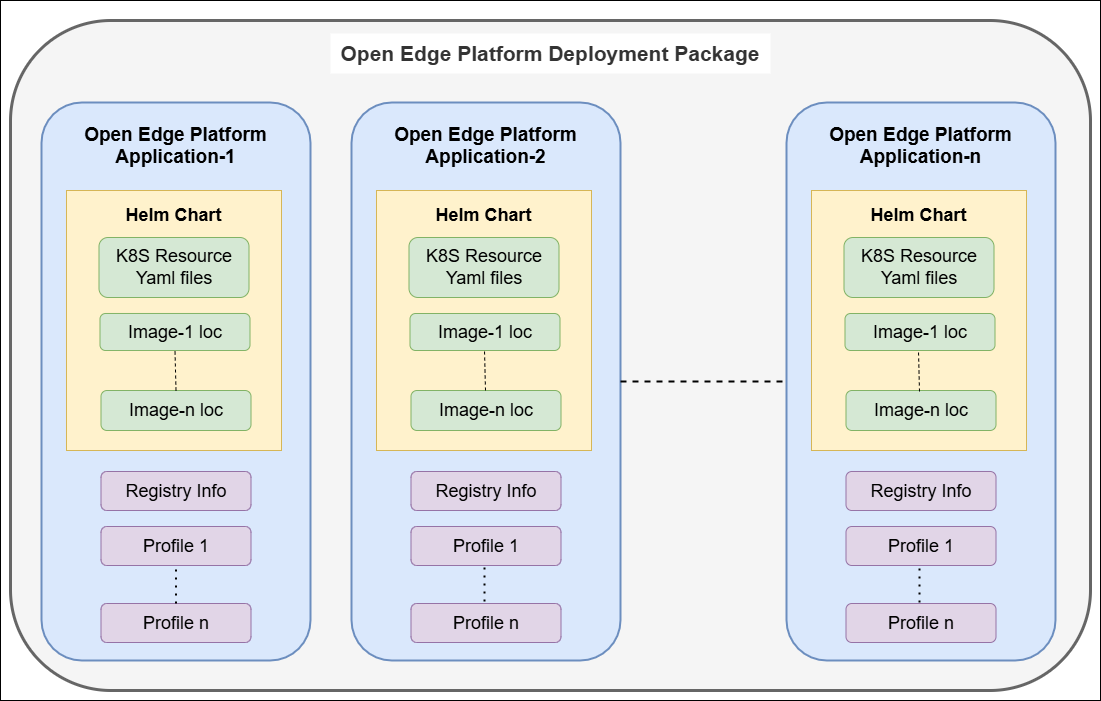
Figure 1: Data Model of Application Orchestration in Open Edge Platform Edge Orchestrator#
Registries#
Registries are links to external or internal OCI Registries that contain the Helm Charts and Container Images that are to be deployed. Applications are associated with a Registry, and at deployment time the Root URL and optionally the credentials and certificate information for the Registry are used to pull the Helm Charts and Container Images.
Deployments#
Deployments are used to take a Deployment Package and schedule it for deployment to a set of edges, according to a policy. Deployments are lifecycle managed, and can be created, deleted, or upgraded. Deployments are runtime instances of Deployment Packages (and therefore Applications) with a chosen Profile and optionally value overrides (parameter templates).
Networks#
Network objects are a CRD that can be used to drive the Interconnect service to connect services in deployed Applications across Edge Node Clusters.
Multi-Tenant Projects#
The multi-tenancy data model of the Edge Orchestrator is based on a two-tier model of Organizations and Projects. All of the above Data Model entities are associated with a Project, which is associated with an Organization. The individual microservices of Application Orchestration are multi-tenant capable, with the ability to isolate data and operations.