Enabling UEFI Secure Boot for Smart Intersection#
UEFI Secure Boot establishes a chain of trust from firmware to OS, cryptographically verifying the signature and hash of all boot components before passing control to the operating system. This ensures the Smart Intersection application runs on a verified, secure platform.
Ubuntu LTS official releases are signed by Canonical, and Canonical’s certificate is pre-enrolled in the MOK (Machine Owner Key) database.
Step 1: Install Required Tools#
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
sudo apt-get install -y openssl mokutil sbsigntool
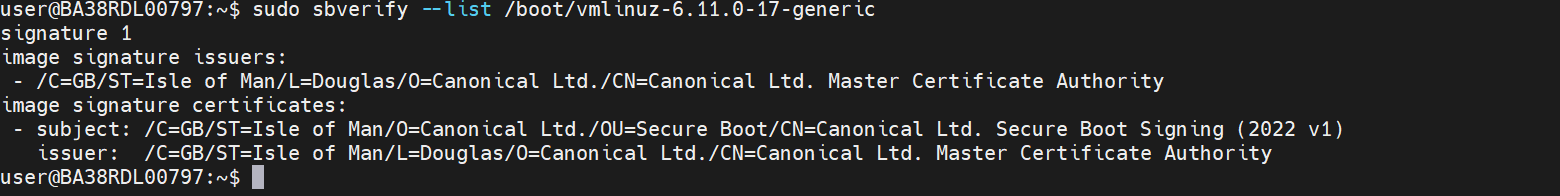
Step 2: Verify Kernel Signature#
sudo sbverify --list /boot/vmlinuz-<kernel_version>-generic
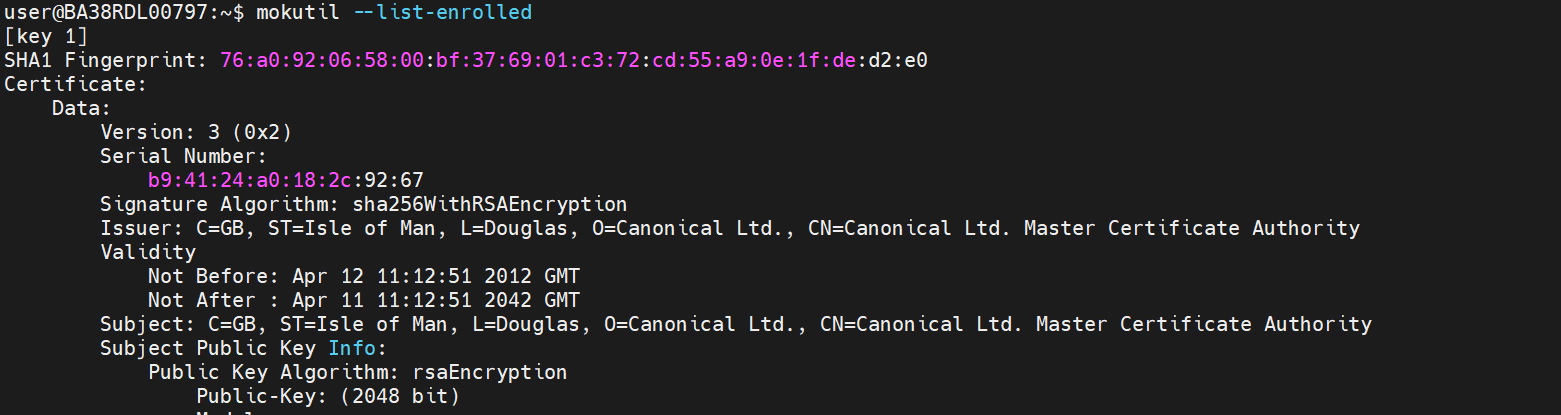
Step 3: Verify Certificate Enrollment
mokutil --list-enrolled
Step 3: Install Signed Shim Binary#
Most UEFI firmware has Microsoft keys enrolled by default. To verify GRUB and Linux kernel signed by Canonical, install the signed shim binary. Shim is a small bootloader signed by Microsoft that bridges the gap between firmware and Linux GRUB, maintaining the chain of trust.
sudo apt-get install sbsigntool openssl grub-efi-amd64-signed shim-signed
sudo grub-install --uefi-secure-boot
Step 4: Configure Secure Boot**#
Reboot the platform and enter the UEFI GUI menu
Verify that Secure Boot is initially disabled
Confirm the shim binary can boot to OS
Step 5: Enroll Microsoft Certificates**#
Get the Secure Boot Microsoft keys and certificates:
git clone https://git.launchpad.net/qa-regression-testing
Enroll the certificates (type ‘y’ when prompted):
cd qa-regression-testing/notes_testing/secure-boot
cp -rf * /tmp
sudo /tmp/sb-setup enroll microsoft
Note: If enrollment errors occur, reboot the platform, boot using
fs0:/efi/ubuntu/shimx64.efi, and rerun the enroll command.
Step 6: Enable and Verify Secure Boot**#
Reboot the platform and enter the BIOS menu
Verify that Secure Boot is now enabled
Boot using
fs0:/efi/ubuntu/shimx64.efiCheck the Secure Boot status after booting to Ubuntu:
mokutil --sb-state

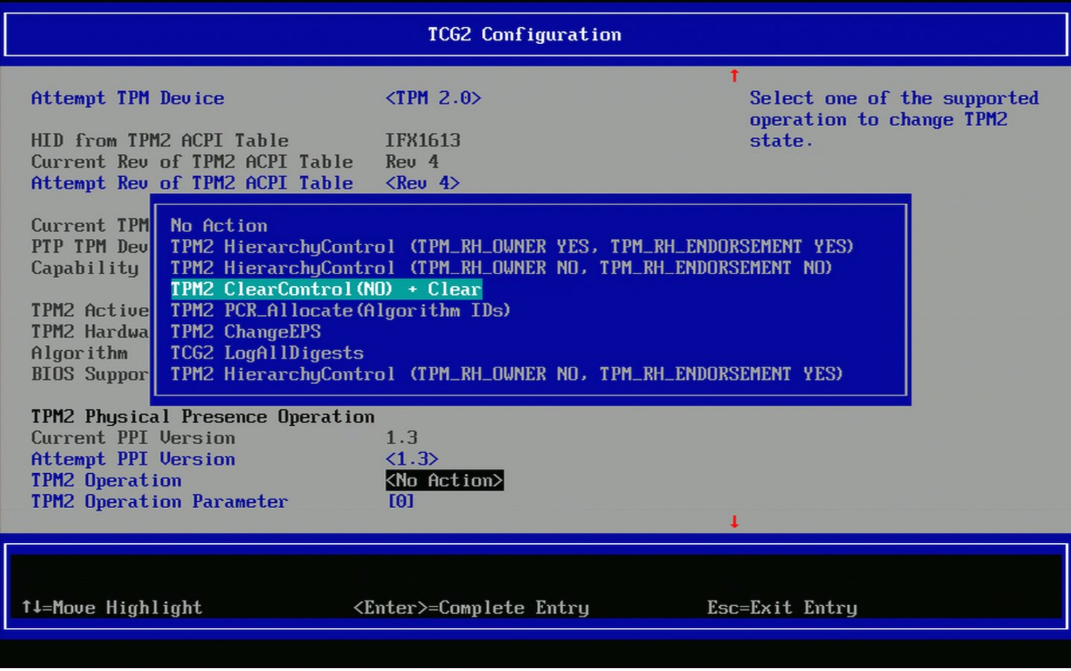
TPM Clear Operation#
TPM clear removes all stored keys, certificates, and ownership data from the Trusted Platform Module, resetting it to factory defaults. This is useful when setting up security for a new Smart Intersection deployment.
Enter the boot manager menu
Choose the TCG2 configuration
Clear the TPM