Visual AI Demo Kit - Tutorial 2#
This tutorial guides you through customizing Node-RED flows to process AI inference data from metro vision applications. You’ll learn how to connect to MQTT data streams, manipulate inference results, add custom business logic, and create enhanced data outputs for downstream systems.
By following this guide, you will learn how to:
Access and Launch Node-RED: Connect to the Node-RED interface and understand the flow-based programming environment
Clear and Reset Flows: Remove existing flows and start with a clean workspace for custom development
Connect to MQTT Data Streams: Establish connections to receive real-time AI inference data from metro vision applications
Implement Custom Data Processing: Add custom names, metadata, and business logic to AI inference results using function nodes
Publish Enhanced Data: Send processed data back to MQTT topics for consumption by other applications
Prerequisites#
Complete Tutorial 1 - AI Tolling System to have a running metro vision AI application
Verify that your metro vision AI application is running and producing MQTT data
Basic understanding of Node-RED flow-based programming concepts
Familiarity with MQTT messaging protocol and JSON data structures
Web browser access to the Node-RED interface
Node-RED Flow Architecture Overview#
The custom Node-RED flow consists of:
MQTT Input Node: Subscribes to AI inference data topics
Function Nodes: Processes and enhances the incoming data with custom logic
Debug Nodes: Provides real-time monitoring of data flow
MQTT Output Node: Publishes enhanced data to new or existing topics
Set up and First Use#
1. Access the Node-RED Interface#
Launch Node-RED in your web browser using your host system’s IP address:
# Find your host IP address if needed
hostname -I | awk '{print $1}'
Open your web browser and navigate to the Node-RED interface:
https://<HOST_IP>/grafana
Replace <HOST_IP> with your actual system IP address.
Troubleshooting Node-RED Access
If you cannot access Node-RED:
Verify the metro vision AI application is running:
docker ps | grep node-red
Check that port 1880 is exposed and accessible
Ensure no firewall is blocking the connection
Try accessing via localhost if running on the same machine:
https://localhost/nodered
2. Clear Existing Node-RED Flows#
Remove any existing flows to start with a clean workspace:
Select All Flows: Press
Ctrl+A(orCmd+Aon Mac) to select all nodes in the current flowDelete Selected Nodes: Press the
Deletekey to remove all selected nodesDeploy Changes: Click the red Deploy button in the top-right corner to save the changes
Go to the URL https://<HOST_IP>/nodered.
Select everything inside the flow and delete it.
This clears the your node red flow.
3. Create MQTT Input Connection#
Set up an MQTT subscriber node to receive AI inference data:
Add MQTT Input Node:
Drag an
mqtt innode from the network section in the left paletteDouble-click the node to configure it
Configure MQTT Broker:
Server:
broker:1883(or your MQTT broker address)Topic:
object_detection_1(or your specific AI data topic)QoS:
0Output:
auto-detect (parsed JSON object, string or buffer)
Set Node Properties:
Name:
AI Inference InputClick Done to save the configuration
4. Add Debug Output for Monitoring#
Create a debug node to monitor incoming data:
Add Debug Node:
Drag a
debugnode from the common sectionConnect the output of the MQTT input node to the debug node input
Configure Debug Node:
Output:
msg.payloadTo:
debug windowName:
Raw Data Monitor
Deploy and Test:
Click Deploy
Check the debug panel (bug icon in the right sidebar) for incoming messages
Restart the AI Pipeline (if needed): If you don’t see data in the debug panel, execute the AI pipeline using this curl command:
curl -k -s https://localhost/api/pipelines/user_defined_pipelines/car_plate_recognition_1 -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d ' { "source": { "uri": "file:///home/pipeline-server/videos/cars_extended.mp4", "type": "uri" }, "destination": { "metadata": { "type": "mqtt", "topic": "object_detection_1", "timeout": 1000 }, "frame": { "type": "webrtc", "peer-id": "object_detection_1" } }, "parameters": { "detection-device": "CPU" } }'
After running this command, you should see AI inference data appearing in the Node-RED debug panel.
5. Implement Custom Data Processing Function#
Add a function node to enhance the AI inference data with custom metadata:
Add Function Node:
Drag a
functionnode from the function sectionPosition it after the MQTT input
Connect the mqtt in node output to this function node
Configure the Function Node:
Name:
Add Custom MetadataOn Message:
// Extract license, color, and type from msg.payload
// Skip frames that don't have all required attributes
// Check if payload exists and has objects array
if (!msg.payload || !msg.payload.metadata.objects || !Array.isArray(msg.payload.metadata.objects)) {
return null; // Ignore this data frame
}
let extractedData = [];
// Process each object in the objects array
for (let obj of msg.payload.metadata.objects) {
// Check if object has all required attributes
if (!obj.license_plate || !obj.color || !obj.type) {
continue; // Skip this object if missing any attribute
}
// Extract the data
let extractedObj = {
license: obj.license_plate.label || null,
color: obj.color.label || null,
type: obj.type.label || null,
// Optional: include confidence scores
color_confidence: obj.color.confidence || null,
type_confidence: obj.type.confidence || null
};
extractedData.push(extractedObj);
}
// If no valid objects found, ignore this data frame
if (extractedData.length === 0) {
return null;
}
// Return the extracted data
msg.payload = extractedData;
return msg;
6. Configure MQTT Output for Enhanced Data#
Set up an MQTT publisher to send the enhanced data:
Add MQTT Output Node:
Drag an
mqtt outnode from the network sectionConnect the function node output to this MQTT output node
Configure MQTT Publisher:
Server: Same as input (
broker:1883)Topic:
enhanced(or usemsg.topicfor dynamic topics)QoS:
0Retain:
falseName:
Enhanced Data Publisher
Add Debug Output:
Add another debug node connected to the Add Custom Metadata function Node
Name:
Enhanced Data Monitor
7. Deploy and Validate the Custom Flow#
Test your custom Node-RED flow:
Deploy the Complete Flow:
Click the Deploy button on the Top Right side in Node-RED interface
Monitor Data Flow:
Open the debug panel in Node-RED
Verify that both raw and enhanced data are flowing through the system
Check timestamps and custom metadata are being added correctly
Expected Results#
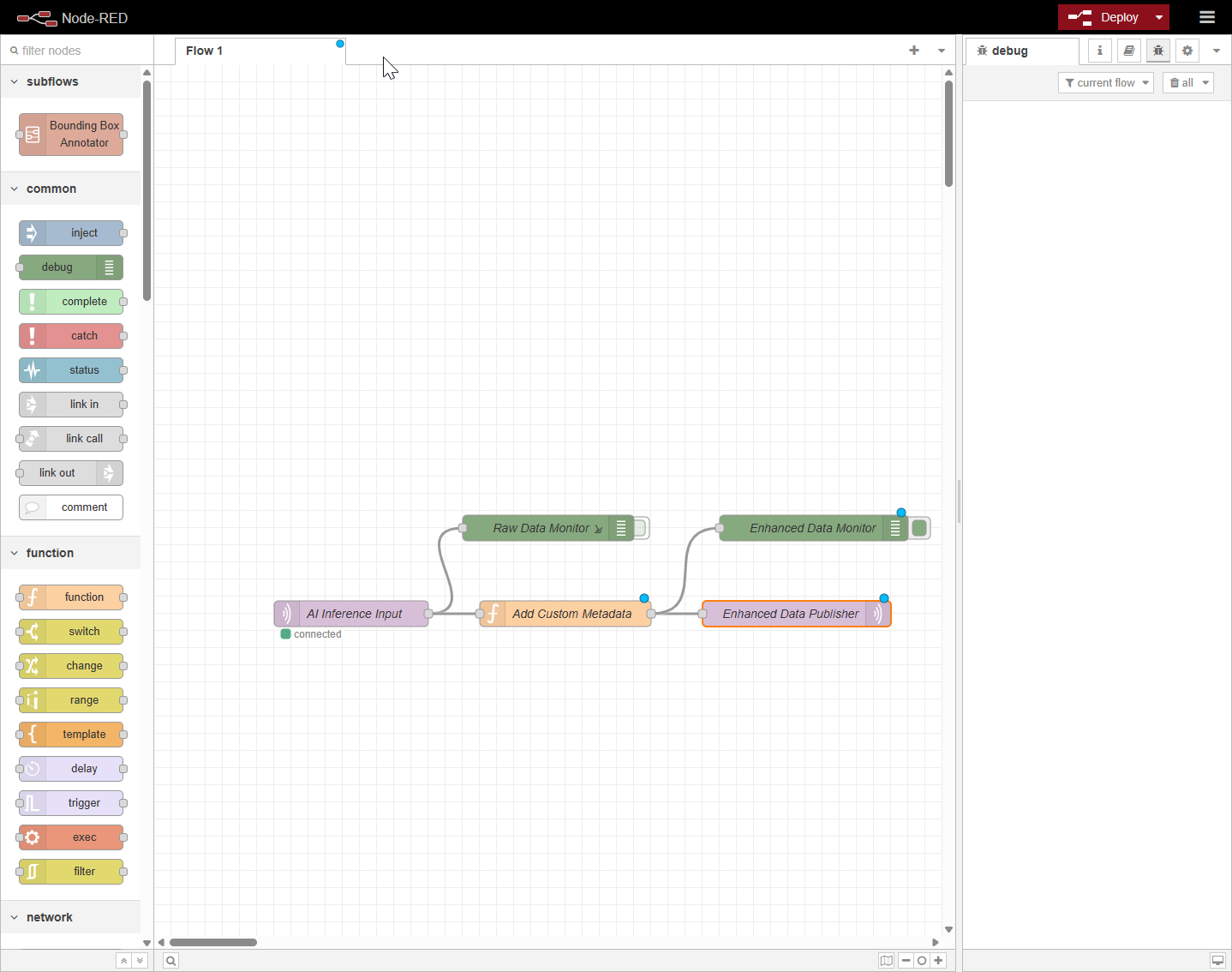
If you are unable to visualize any data, try restarting the inference pipeline.
After completing this tutorial, you should have:
Custom Node-RED Flow: A working flow that processes AI inference data with custom enhancements
Enhanced Data Stream: MQTT topics publishing enriched data with custom metadata
Real-time Monitoring: Debug panels showing data flow and transformations
Flexible Architecture: A foundation for adding more complex business logic and data processing
Next Steps#
After successfully setting up the AI Tolling system with Node Red, consider these enhancements:
Troubleshooting#
Node-RED Interface Not Accessible#
Problem: Cannot access Node-RED at the specified URL
Solution:
# Check if Node-RED container is running docker ps | grep node-red # Restart the metro vision AI application if needed ./sample_stop.sh && ./sample_start.sh
No Data in Debug Panel#
Problem: Debug nodes show no incoming data
Solution:
Verify the AI application is running and generating inference data
Check MQTT topic names match your application’s output topics
Ensure proper JSON parsing in function nodes
Function Node Errors#
Problem: Function node shows errors in the debug panel
Solution:
Add try-catch blocks around JSON parsing
Use
node.warn()ornode.error()for debuggingValidate input data structure before processing