Get Started#
Time to Complete: 30 minutes
Programming Language: Python 3
Configure Docker#
To configure Docker:
Run Docker as Non-Root: Follow the steps in Manage Docker as a non-root user.
Configure Proxy (if required):
Set up proxy settings for Docker client and containers as described in Docker Proxy Configuration.
Example
~/.docker/config.json:{ "proxies": { "default": { "httpProxy": "http://<proxy_server>:<proxy_port>", "httpsProxy": "http://<proxy_server>:<proxy_port>", "noProxy": "127.0.0.1,localhost" } } }
Configure the Docker daemon proxy as per Systemd Unit File.
Enable Log Rotation:
Add the following configuration to
/etc/docker/daemon.json:{ "log-driver": "json-file", "log-opts": { "max-size": "10m", "max-file": "5" } }
Reload and restart Docker:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl restart docker
Clone source code#
git clone https://github.com/open-edge-platform/edge-ai-suites.git
git checkout release-2025.2.0
cd edge-ai-suites/manufacturing-ai-suite/industrial-edge-insights-time-series
Deploy with Docker Compose#
Update the following fields in
.env:INFLUXDB_USERNAMEINFLUXDB_PASSWORDVISUALIZER_GRAFANA_USERVISUALIZER_GRAFANA_PASSWORD
Deploy the sample app, use only one of the following options:
NOTE:
The below
make up_opcua_ingestionormake up_mqtt_ingestionfails if the above required fields are not populated as per the rules called out in.envfile.The sample app is deployed by pulling the pre-built container images of the sample app from the docker hub OR from the internal container registry (login to the docker registry from cli and configure
DOCKER_REGISTRYenv variable in.envfile atedge-ai-suites/manufacturing-ai-suite/industrial-edge-insights-time-series)The
CONTINUOUS_SIMULATOR_INGESTIONvariable in the.envfile (for Docker Compose) and inhelm/values.yaml(for Helm deployments) is set totrueby default, enabling continuous looping of simulator data. To ingest the simulator data only once (without looping), set this variable tofalse.If
CONTINUOUS_SIMULATOR_INGESTIONis set tofalse, you may see the[inputs.opcua] status not OK for nodemessage in thetelegraflogs for OPC-UA ingestion after a single data ingestion loop. This message can be ignored.
make up_opcua_ingestionis supported only forWind Turbine Anomaly Detectionsample app
:sync: tab1
Using OPC-UA ingestion:
make up_opcua_ingestion app="wind-turbine-anomaly-detection"
Using MQTT ingestion:
make up_mqtt_ingestion app="wind-turbine-anomaly-detection"
:sync: tab2
make up_mqtt_ingestion app="weld-anomaly-detection"
Multi-Stream Ingestion support#
Multi-stream ingestion enables the simultaneous processing of multiple data streams, improving throughput and scalability.
To activate multi-stream ingestion, set the num_of_streams parameter to the required number of parallel streams when deploying the application.
<NUMBER_OF_STREAMS>: Specify the number of parallel streams to run (e.g., 3 for three concurrent streams).
:sync: tab1
# Deploy with OPC-UA Multi-Stream Ingestion
make up_opcua_ingestion app="wind-turbine-anomaly-detection" num_of_streams=<NUMBER_OF_STREAMS>
# Deploy with MQTT Multi-Stream Ingestion
make up_mqtt_ingestion app="wind-turbine-anomaly-detection" num_of_streams=<NUMBER_OF_STREAMS>
:sync: tab2
# Deploy with MQTT Multi-Stream Ingestion
make up_mqtt_ingestion app="weld-anomaly-detection" num_of_streams=<NUMBER_OF_STREAMS>
Notes#
Ensure system resources (CPU, memory) are sufficient to support the desired number of streams.
For troubleshooting or monitoring, use
make statusto verify container health and logs.Note: The command
make statusmay show errors in containers like ia-grafana when user have not logged in for the first login OR due to session timeout. Just login again in Grafana and functionality wise if things are working, then ignoreuser token not founderrors along with other minor errors which may show up in Grafana logs.make status
Running User Defined Function(UDF) inference on GPU#
By default, UDF for both the sample apps is configured to run on CPU.
The Wind Turbine Anomaly Detection sample app ML model can run on GPU while
the Weld Anomaly Detection sample app ML model can only run on CPU.
To trigger the UDF inference on GPU in Time Series Analytics Microservice, run the following command:
curl -k -X 'POST' \
'https://<HOST_IP>:3000/ts-api/config' \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '<Add contents of edge-ai-suites/manufacturing-ai-suite/industrial-edge-insights-time-series/apps/wind-turbine-anomaly-detection/time-series-analytics-config/config.json with device
value updated to gpu from cpu>'
Verify the Output Results#
:sync: tab1
Get into the InfluxDB* container:
Note: Use
kubectl exec -it <influxdb-pod-name> -n <namespace> -- /bin/bashfor the helm deployment where forreplace with namespace name where the application was deployed and for replace with InfluxDB pod name. docker exec -it ia-influxdb bash
Run following commands to see the data in InfluxDB*:
NOTE: Please ignore the error message
There was an error writing history file: open /.influx_history: read-only file systemhappening in the InfluxDB shell. This does not affect any functionality while working with the InfluxDB commands# For below command, the INFLUXDB_USERNAME and INFLUXDB_PASSWORD needs to be fetched from `.env` file # for docker compose deployment and `values.yml` for helm deployment influx -username <username> -password <passwd> use datain # database access show measurements # Run below query to check and output measurement processed # by Time Series Analytics microservice select * from "wind-turbine-anomaly-data"
To check the output in Grafana:
Use link
https://<host_ip>:3000/to launch Grafana from browser (preferably, chrome browser)Note: Use link
https://<host_ip>:30001to launch Grafana from browser (preferably, chrome browser) for the helm deploymentLogin to the Grafana with values set for
VISUALIZER_GRAFANA_USERandVISUALIZER_GRAFANA_PASSWORDin.envfile.
After login, click on Dashboard
Select the
Wind Turbine Dashboard.
You will see the below output.
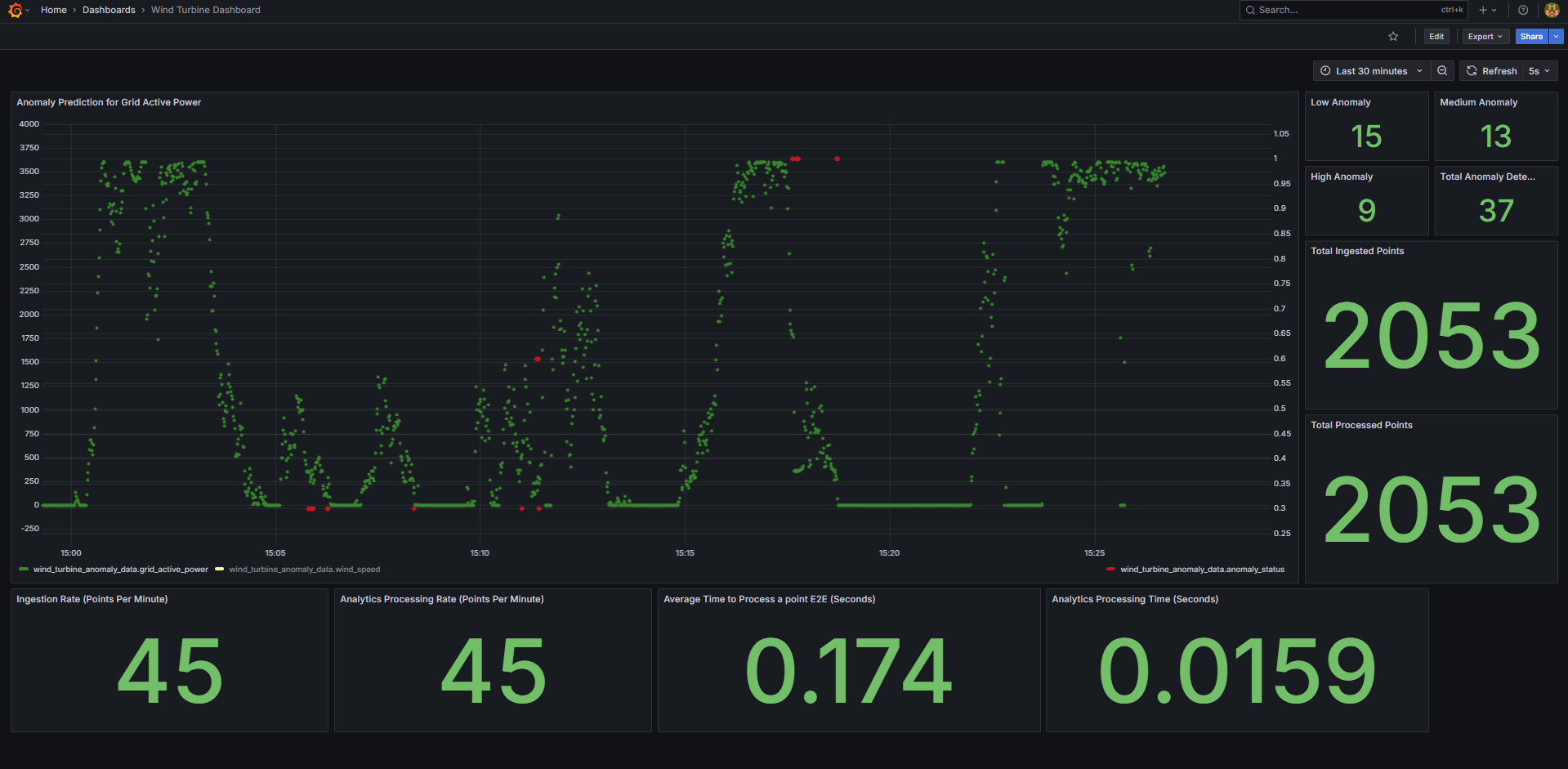
:sync: tab2
Get into the InfluxDB* container:
Note: Use
kubectl exec -it <influxdb-pod-name> -n <namespace> -- /bin/bashfor the helm deployment where forreplace with namespace name where the application was deployed and for replace with InfluxDB pod name. docker exec -it ia-influxdb bash
Run following commands to see the data in InfluxDB*:
NOTE: Please ignore the error message
There was an error writing history file: open /.influx_history: read-only file systemhappening in the InfluxDB shell. This does not affect any functionality while working with the InfluxDB commands# For below command, the INFLUXDB_USERNAME and INFLUXDB_PASSWORD needs to be fetched from `.env` file # for docker compose deployment and `values.yml` for helm deployment influx -username <username> -password <passwd> use datain # database access show measurements # Run below query to check and output measurement processed # by Time Series Analytics microservice select * from "weld-sensor-anomaly-data"
To check the output in Grafana:
Use link
https://<host_ip>:3000/to launch Grafana from browser (preferably, chrome browser)Note: Use link
https://<host_ip>:30001to launch Grafana from browser (preferably, chrome browser) for the helm deploymentLogin to the Grafana with values set for
VISUALIZER_GRAFANA_USERandVISUALIZER_GRAFANA_PASSWORDin.envfile.
After login, click on Dashboard

Select the
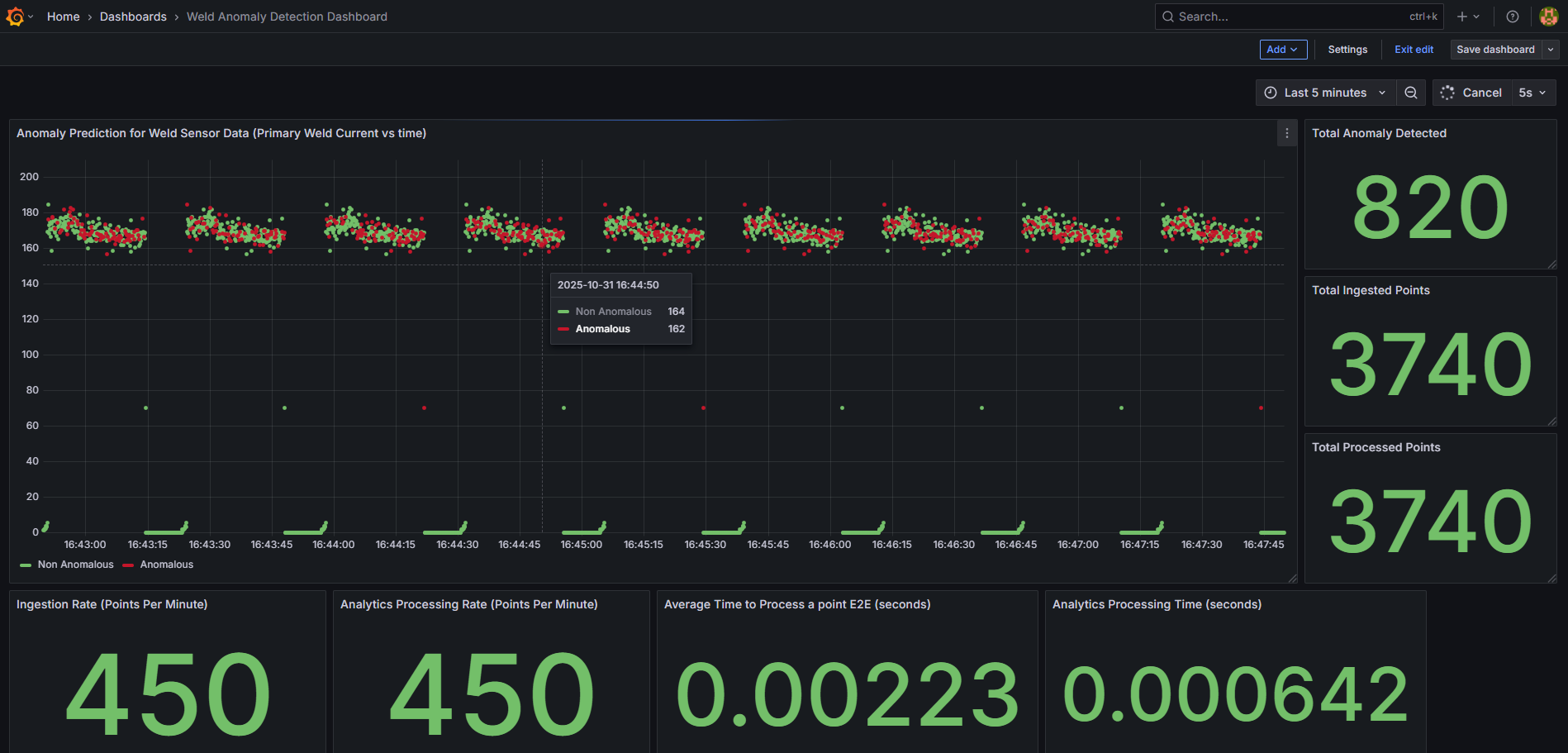
Weld Anomaly Detection Dashboard.
One will see the below output.
Bring down the sample app#
make down
Check logs - troubleshooting#
Check container logs to catch any failures:
docker ps
docker logs -f <container_name>
docker logs -f <container_name> | grep -i error
Other Deployment options#
See How to Deploy with Helm guide to learn how to deploy the sample application on a k8s cluster using Helm.
Advanced setup#
How to build from source and deploy: Guide to build from source and docker compose deployment
How to configure OPC-UA/MQTT alerts: Guide for configuring the OPC-UA/MQTT alerts in the Time Series Analytics microservice
How to configure custom UDF deployment package: Guide for deploying a customized UDF deployment package (udfs/models/tick scripts)