Tutorials#
These tutorials demonstrate how to use the Visual Search and QA reference implementation.
Use your own dataset for searching
Filtered search
Configurable parameters
Tutorial 1: Use your own dataset for searching#
In this tutorial, you will learn how to use your own dataset for searching.
Learning objectives
By the end of this tutorial, you will be able to ingest your own dataset to vector DB and conduct search and QA based on them.
Step 1: Put the dataset under designated host directory#
Check
env.shwhich is sourced before executingdocker compose, findHOST_DATA_PATH, which should be pre-created according to Get Started.export HOST_DATA_PATH="$HOME/data"
Put your dataset (including images and videos) under this directory
Step 2: ingest the dataset to vector DB#
Deploy the application
Go to the web UI, fill in
file directory on hostwith the absolute path to your dataset directory, and clickUpdateDB
Summary
In this tutorial, you learned how to use your own dataset for searching.
Tutorial 2: Filtered search#
In this tutorial, you will learn how to ingest data along with metadata to support filtered search
Learning objectives
By the end of this tutorial, you will be able to ingest data with metadata by providing matched metadata json file for each media data file in the
file directory on hostused for updating DBBy the end of this tutorial, you will be able to manually ingest single data file with specified metadata using dataprep microservice API
By the end of this tutorial, you will be able to conduct filtered search on web UI
Step 1: Prepare metadata json file#
When processing data files in
file directory on host(for simplicity, noted as<host_data_path>in the following steps), the dataprep microservice automatically looks for a json file in<host_data_path>/metawith the same basename with the file that is being processing. For example, when processing file ``<host_data_path>/image123.png, it looks for a<host_data_path>/meta/image123.json`. If found, the fields in the json file would be recorded into the vector DB along with the media file as its metadata.In the web UI, two example fields are supported:
cameraandtimestamp. An example json is like:{ "camera": "camera_1", "timestamp": 20250101 }
Here is an example python function to generate fake metadata json files given the file directory
def generate_fake_meta(file_dir): if not os.path.isdir(file_dir): raise ValueError(f"The provided path '{file_dir}' is not a valid directory.") timestamp = datetime.date(2025, 1, 1) timestamp = int(timestamp.strftime("%Y%m%d")) # 20250101 cnt = 1 month = 1 meta_dir = os.path.join(file_dir, "meta") os.makedirs(meta_dir, exist_ok=True) for root, _, files in os.walk(file_dir): if root.split("/")[-1] == "meta": continue for file_name in files: file_path = os.path.join(root, file_name) # Skip directories, only process files if os.path.isfile(file_path): # Generate the JSON file name base_name, _ = os.path.splitext(file_name) json_file_path = os.path.join(meta_dir, f"{base_name}.json") fake_label = f"camera_{cnt}" timestamp = datetime.date(2025, month, cnt % 30 + 1) # Increment day, reset to 1 if exceeds 30 fake_timestamp = int(timestamp.strftime("%Y%m%d")) fake_meta = { "camera": fake_label, "timestamp": fake_timestamp } cnt += 1 if cnt > month*30: month += 1 # Write the JSON content to the file with open(json_file_path, "w") as json_file: json.dump(fake_meta, json_file, indent=4)
Also, you may try using the dateprep microservice API to manually ingest a single data file with given metadata, for example:
# if it is already ingested, delete first curl -X DELETE "http://10.67.106.227:9990/v1/dataprep/delete?file_path=<path_to_your_file.mp4>" # re-ingest with metadata curl -X POST "http://${host_ip}:${DATAPREP_SERVICE_PORT}/v1/dataprep/ingest" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "file_path": <path_to_your_file.mp4>, "meta": {"camera": "camera_7"} }'
Step 2: Use metadata as filter on web UI#
Once the metadata is available, it can be used for filtered search
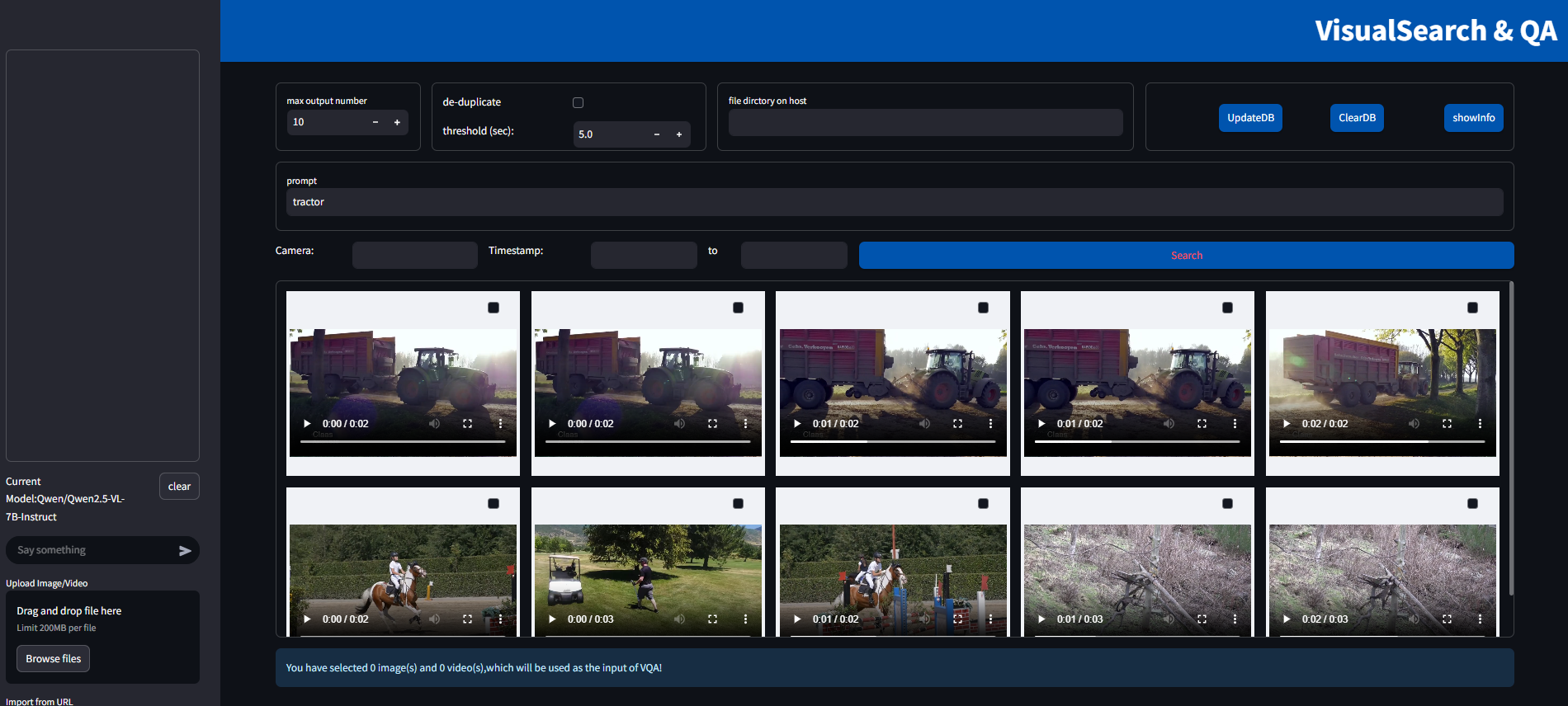
Figure 1: Search without filter
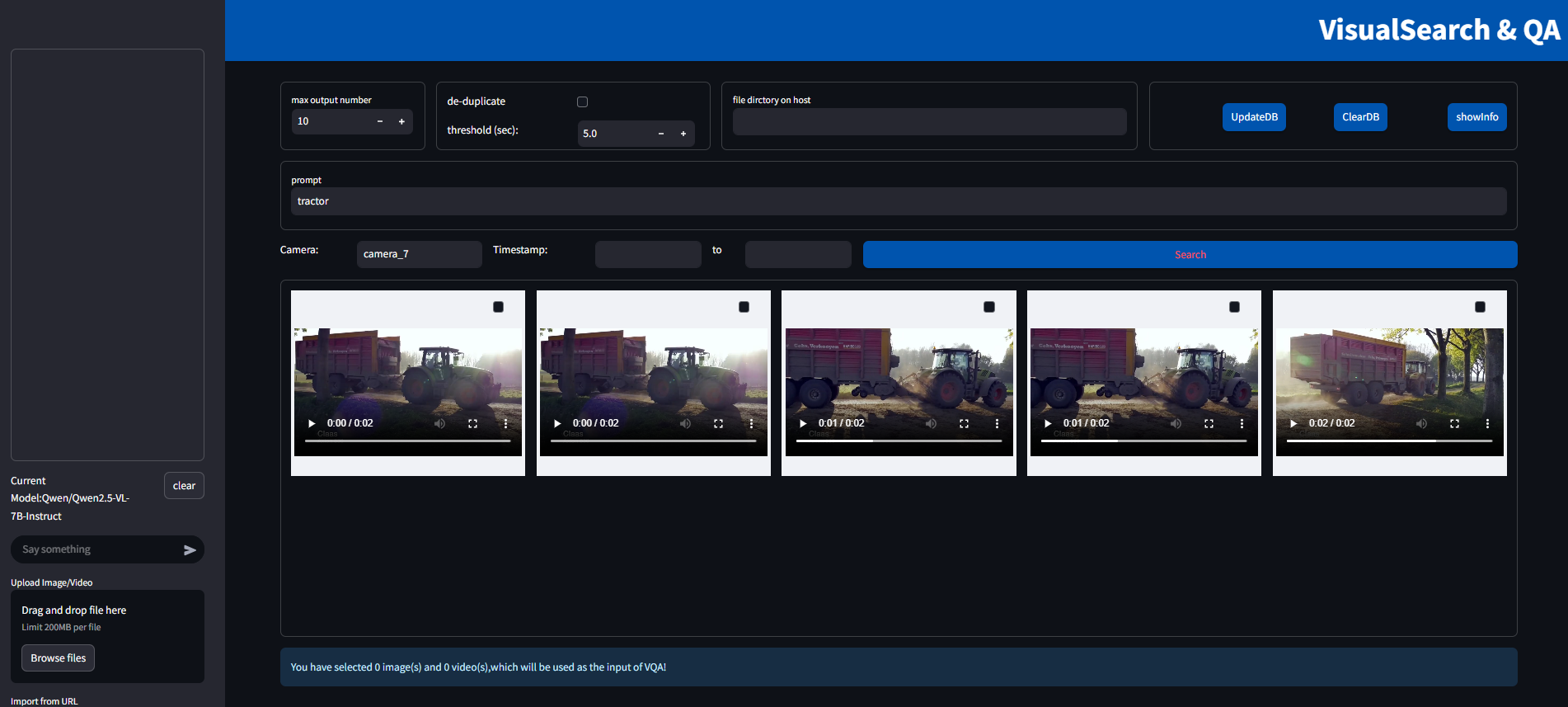
Figure 2: Search with filter
Supported filters#
Summary
In this tutorial, you learned how to: ingest data with metadata (both via providing a json file or via API), and search with filters enabled
Tutorial 3: Configurable parameters#
In this tutorial, you will learn how to adjust the configuarable parameters for the application
Learning objectives
By the end of this tutorial, you will be able to know which parameters to modify when needed
Configurable parameters#
The number of results shown per row in UI layout: default as 5. Change it by exporting this environment variable and re-deploy the application
export SHOW_RESULT_PER_ROW=10
Deduplicate switch and threshold: deduplicate switch decides whether or not to enable deduplication for similar search results. Note that this function currently supports video only. Once enabled, video search results that are the same video and start within the interval of threshold would be deduplicated. Only one remains. For example:
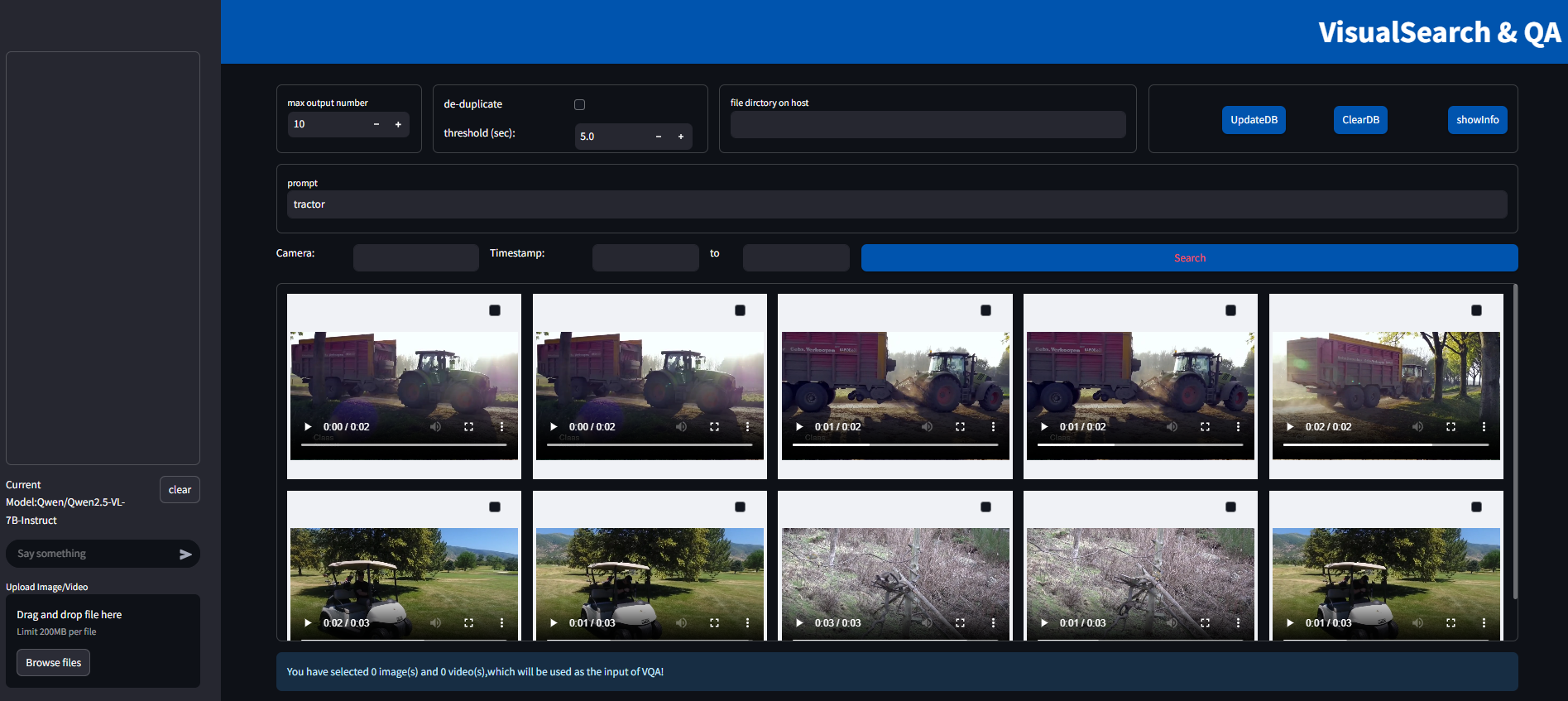
Figure 1: Search without deduplication
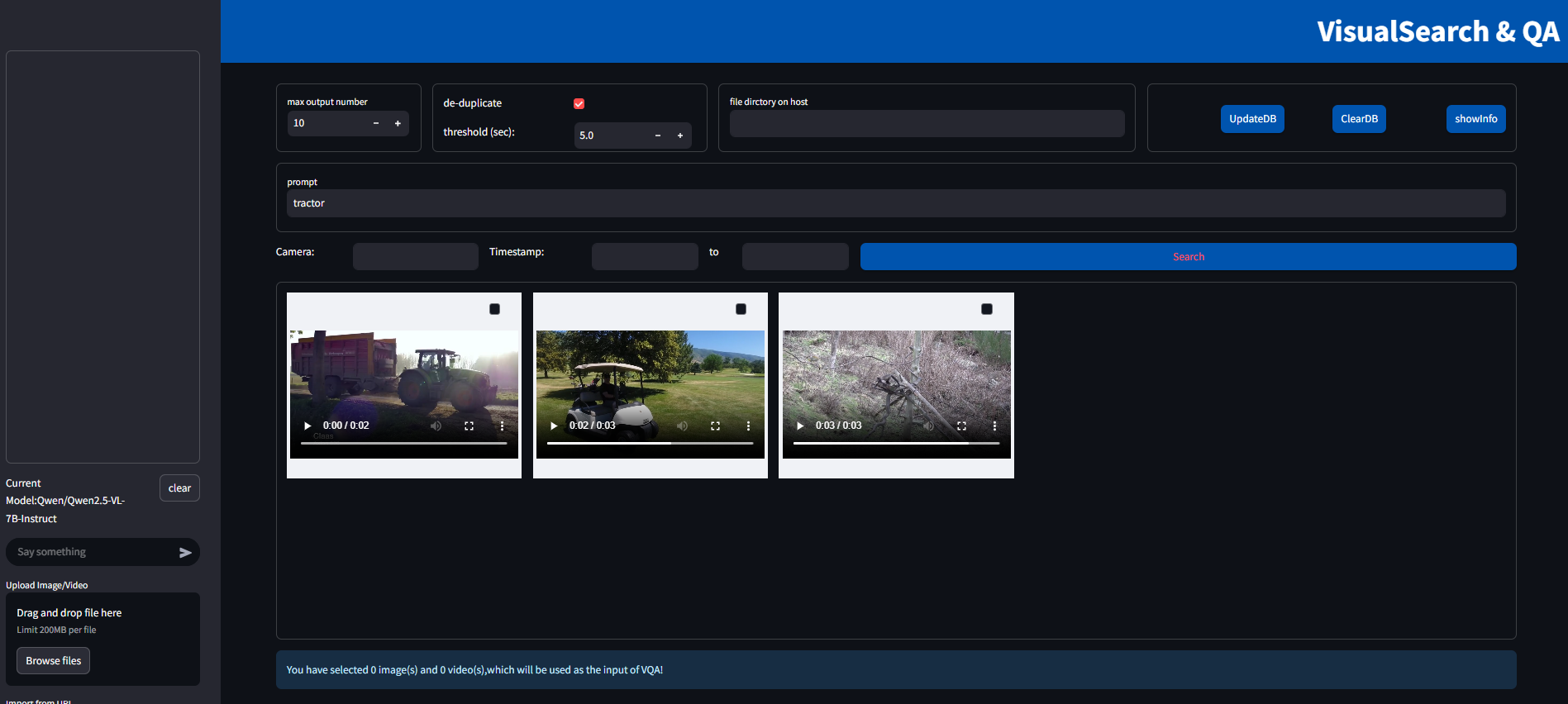
Figure 2: Search with deduplication
Without deduplication enabled, the first row of results are from the same video, and the time difference among them are less than 5 seconds. Therefore, when deduplication is ticked, search button returns only one result from that video.
Learn More#
Deploy the application with the Get Started.
Understand the components, services, architecture, and data flow, in the Overview.