Overview#
Unified analytics of a traffic intersection
The Smart Intersection Sample Application uses edge AI technologies to improve traffic management at intersections. Multiple traffic cameras work together to create a complete view of the intersection.
The application tracks objects across different camera angles. It analyzes vehicle speed and direction and understands how objects interact in real space. Existing cameras can power this system without replacement. The solution provides real-time insights from multiple cameras simultaneously. This approach transforms individual camera feeds into smart, coordinated traffic monitoring.
Example Use Cases#
Pedestrian Safety: Enhance safety for people crossing the street.
The system tracks pedestrians at crosswalks. It alerts when people walk outside safe crossing areas.
Traffic Flow Monitoring: Count vehicles and measure dwell time in each lane.
The system detects when vehicles stay too long in lanes. This identifies stalled cars, accidents, and traffic jams.
Key Benefits#
The key benefits are as follows:
Multi-camera multi-object tracking: Enables tracking of objects across multiple camera views.
Scene based analytics: Regions of interest that span multiple views can be easily defined on the map rather than independently on each camera view. This greatly simplifies business logic, enables more flexibility in defining regions, and allows various types of sensors to be used to track vehicles and people such as lidar and radar in addition to cameras.
Improved Urban Management: Object tracks and analytics are available near-real-time on the MQTT broker to enable actionable insights for traffic monitoring and safety applications.
Reduced TCO: Works with existing cameras, simplifies business logic development, and future-proofs the solution by enabling additional sensors and cameras as needed without changing the business logic.
How it Works#
This section provides a high-level view of how the application integrates with a typical system architecture.
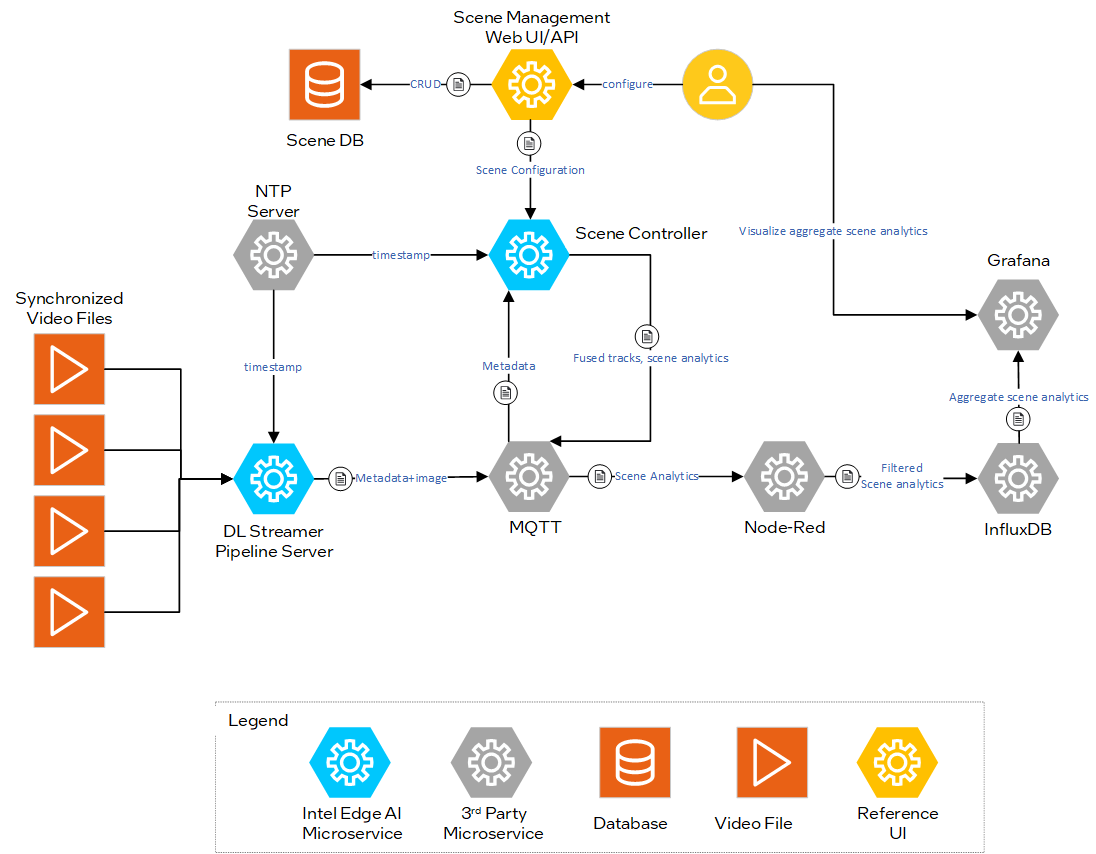
Example Content for Diagram Description#
Inputs:
Video Files - Four traffic intersection cameras that capture videos simultaneously.
Scene Database - Pre-configured intersection scene with satellite view of intersection, calibrated cameras, and regions of interest.
The video recordings are used to simulate the live feed from cameras deployed at a traffic intersection. The application can be configured to work with live cameras.
Processing:
Video Analytics - Deep Learning Streamer Pipeline Server (DL Streamer Pipeline Server) utilizes a pre-trained object detection model to generate object detection metadata and and a local NTP server for synchronized timestamps. This metadata is published to the MQTT broker
Sensor Fusion - Scene Controller Microservice fuses the metadata from video analytics utilizing scene data obtained through the Scene Management API. It uses the fused tracks and the configured analytics (regions of interest) to generate events that are published to the MQTT broker.
Aggregate Scene Analytics - Region of interests analytics are read from the MQTT broker and stored in an InfluxDB bucket that enables time series analysis through Flux queries.
Outputs:
Fused object tracks are available on the MQTT broker and visualized through the Scene Management UI.
Aggregate scene analytics are visualized through a Grafana dashboard.
Key Features#
Feature 1: Architecture based on modular microservices enables composability and reconfiguration.
Feature 2: Optimized video pipelines for Intel edge devices.
Feature 3: Scene-based analytics allow insights beyond single sensor views.
Learn More#
System Requirements: Check the hardware and software requirements for deploying the application.
Get Started: Follow step-by-step instructions to set up the application.
How to Deploy with Helm: How to deploy the application using Helm on a Kubernetes cluster.
Support and Troubleshooting: Find solutions to common issues and troubleshooting steps.